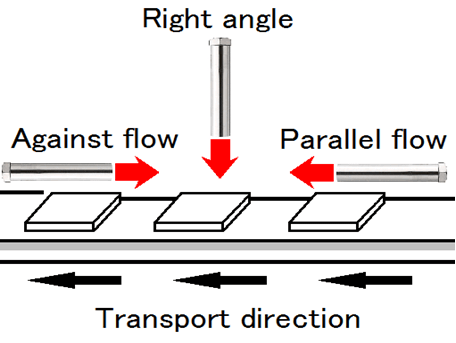
열풍이 자료에 평행하게 흐르는 (순풍) 경우
자료 입구 부근에서 고온 열풍과 접촉하기 위해 건조 속도가 크고, 그 급속히 감소합니다.
재료 예열 기간 및 표면 증발 기간에 재료가 고온 열풍과 접촉하기 위해 고온 열풍을 사용할 수 있습니다.
열효율은 높아지지만 높은 건조 재료를 만들기 위해 장비가 커집니다.
과열에 민감한 재료를 건조하는 경우에 적합합니다.
열풍이 자료에 직각으로 분사 경우
재료 열풍을 균일하게 충돌하는 충돌 제트를 사용하면 기체 경계 막이 얇아지고
열전달율 h와 물질 이동 계수 k를 크게 할 수 있으므로 고정 율 건조 속도를 빠르게 할 수 있습니다.
열풍이 자료에 역행하는 (역풍) 경우
재료 출구 부근에서 고온 열풍과 접촉 물자 입구에서 열풍의 온도가 낮아집니다.
장치 내의 통해 비교적 일정한 건조 속도입니다.
비교적 작은 장치에서 재료의 건조 속도를 높일 수 있습니다.
감소 비율 건조 기간에서 고온 열풍과 접촉하는 재료의 열화 방지를 위해 고온 열풍을 사용하는 것은 피하는 것이 좋다고 생각됩니다.
내열성이있는 재료를 높은 건조하는 경우에 적합합니다.
분무 건조
식품이나 세제 등의 건조에 이용되고 있습니다.
초기 함수율이 높은 재료이므로 재료 단위 질량 당 열 비용은 크지 만 건조 시간이 짧고 열 변성 물질도 품질을 유지하기 쉬운 방법입니다.
식품이나 세제 등의 건조에 이용되고 있습니다.