INDEX

Synthetic resin
In ancient times, “resin” was meant to solid tree sap, such as pine resin and cedar resin.
The word “resin” has been applied in the modern world to nearly any component of a liquid that will set into a hard lacquer or enamel-like finish. An example is nail polish, a modern product which contains “resins” that are organic compounds, but not classical plant resins. Certain “casting resins” and synthetic resins (such as epoxy resin) have also been given the name “resin” because they solidify in the same way as some plant resins, but synthetic resins are liquid monomers of thermosetting plastics, and do not derive from plants.
Plastic
Plastics is Greek originally and molding and Π λ α σ τ ι κό which makes the sense to say are derived from a word asς.
Molding is to make an image with the soft material of the clay.
Latin borrowed that, and it was plasticus, and more English borrowed, and was plastic.
A film, paint and glue are also regarded as plastics from the operation mode top.
Plastics are produced from a variety of raw materials: wood, coal, petroleum, plants,vegetable juices, and proteins.
In some respects, they are superior to comparable natural products because they are produced under scientifically controlled conditions and can be given specific properties not found in nature.
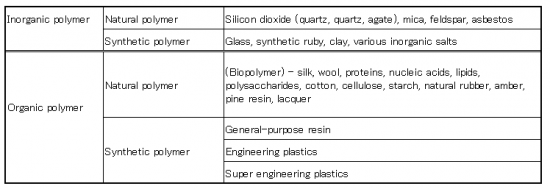
Classification of the polymer compound
General-purpose resin, Engineering plastics and Super engineering plastics, are distinguished by the deflection temperature under load (DTUL) as a measure of the heat resistance.
Engineer plastics are classified as DTUL 100 ℃ or more resins.
Super engineering plastics are classified as DTUL 150 ℃ or more resins.
Synthetic polymer might be classified as synthetic resin, synthetic fiber, synthetic rubber.
Synthetic resins and Synthetic fibers are distinguished in the form of products,
Synthetic resins and Synthetic rubbers are distinguished by the elasticity of the product.
Polymer
Synthetic resin is a kind of polymer compound.
Polymer has a distinctive nature that is different from the low molecular weight, especially mechanical solid or solution, thermodynamic properties can vary greatly.
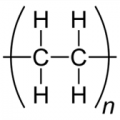
The degree of polymerization of polyethylene ethylene 500 led (1000 carbon atoms) is 500.
As the degree of polymerization increases, it will be harder than the strong resin.
Since polyethylene flow is melted upon the application of heat, and then molded by the state.
The flow then begins to temperature (melting point) will be higher as the molecular weight increases.
When the molecular weight is increased to more than a certain, heat without it over even flow, and then decomposes on further raising the temperature.
For example, polyethylene is a polymer that connects multiple two ethylene carbons, ethylene in this case is referred to as “monomer”, the polyethylene is called “polymers”.
“””Mono””is one, “”poly”” is a prefix that means a lot. A reaction that will connect the monomer is referred to as a polymerization reaction, is called the number of monomers are connected to the degree of polymerization.”
Polymer (macromolecule), the low molecular weight compounds (low molecule weight compound) of the led repeated (polymerized) things, molecular weight refers to the 10,000 or more compounds.
Not only synthetic resin, also it includes natural materials.
The (mono) of monomers is a word derived from the Greek word meaning “one.”
The (poly) of polymer is a word derived from the Greek word meaning “a lot”.
The (homo) of homopolymer is a word derived from the Greek word meaning “same quality”.
The (co) of copolymer is a word derived from the Latin word meaning “together”.
A polymer of a broad sense indicates the polymer with which more than 2 monomers connected.
A polymer of a narrow sense indicates the high polymer with which more than 10000 or more monomers connected.
It is used in much the same meaning almost as a macromolecule.
It seems that the area called a polymer is limited to synthetic resin.
We called the oligomer that a relatively small number of monomer is bound polymer.
Depending on the number of monomers, sometimes referred to as such dimers, trimer, tetramer.
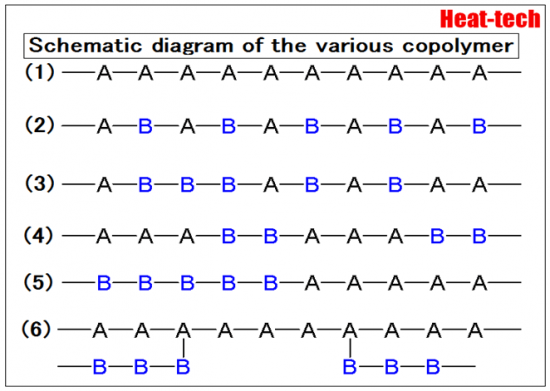
Something made from 1 kind of monomer is called a homopolymeric.
Something made from 2 kinds of monomer is called a copolymer.
Something made from 3 kinds of monomer is called a terpolymer.
For example the ABS resin used by interior of a car possesses high strength and impact resistance by an abbreviation of acrylonitrile butadiene styrene resin of terpolymer (ternary copolymer).
The ABS resin has the strength and impact resistance by combining two properties.
Acrylonitrile resin and Styrene resin which are hard but weakly in an impact.
Butadiene resin which is soft but strong in an impact.
- General homopolymer (homopolymer)
- Alternating copolymer – two kinds of monomers copolymerizable lined alternately
- Random copolymer – copolymer no order to the sequence of the monomer
- Cyclic copolymers – two types are arranged alternately in a cycle where there is a monomer copolymerizable cross
- Block copolymer – copolymerized monomer continuous long of the same type
- Graft copolymer – other polymers arranged as branches in places in the copolymerization to be a stem
Element that has the ability to connect the large number of atoms in the covalent bond is the main chain.
The main chain is mainly limited such as carbon, silicon and oxygen.
The one which made the carbon main chain cable is called organic compound.
The one which has something others the carbon in main chain is called inorganic polymer.
Material of the polymer
Product obtained by distillation from crude oil is the most low-molecular-weight.
In the petrochemical, gasoline fellow naphtha (C6 ~ C8) in the raw material, it can create a synthetic resin is polymerized.
Binding and basic molecules of carbon
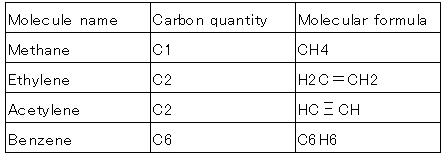
Average molecular of petroleum products
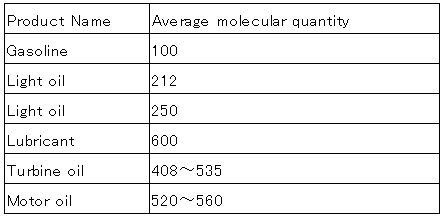
 HEAT-TECH Best Technology Online Shop
HEAT-TECH Best Technology Online Shop