INDEX
Basic principle
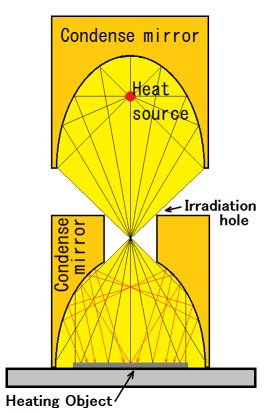
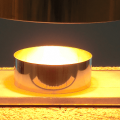
A dome cover is used when heating a relatively wide area or heating a plate-like material uniformly.
If the dome cover needs to be durable, our condense mirrors can also be used as a dome cover.
The light energy irradiated from the irradiation hole is irradiated onto the heated object and a portion is absorbed.
In general, highly reflective materials reflect light energy and do not generate high temperatures.
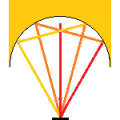
In the case of dome heating, unabsorbed light energy is re-reflected, scattered, and absorbed multiple times within the dome.
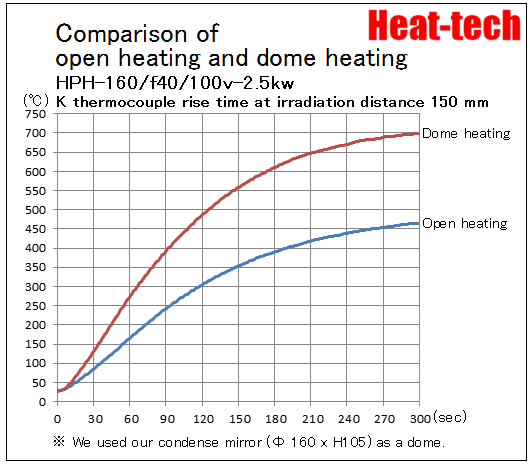
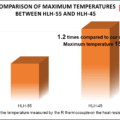
Repeated reflections and absorptions result in higher temperatures compared to open heating.
Non-oxidizing heating can be performed by filling the dome with inert gas.
This heating method is particularly effective for conveying equipment that operates intermittently, such as index tables.
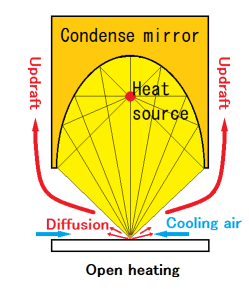
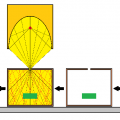
Preventing adverse effects of updraft
Open heating also heats the air around the object to be heated, causing the air to expand thermally and become lighter, creating an updraft.
Air at normal temperature and normal pressure flows into the space that has become lean and low pressure due to the updraft.
This flowing air comes into contact with the object to be heated and cools it down to room temperature, which is not good for heating work.
Frame heating does not generate a flow of cooling air, creating an effective heating environment.
 HEAT-TECH Best Technology Online Shop
HEAT-TECH Best Technology Online Shop