INDEX
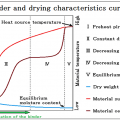
Even if it tells “dryness” to a mouthful, there are three kinds of dry work.
They are dryness of surface water of adhesion, dryness of the coating film, and internal dryness of material.
Since the preceding sections has explained the internal dryness, this section explains the surface dryness.
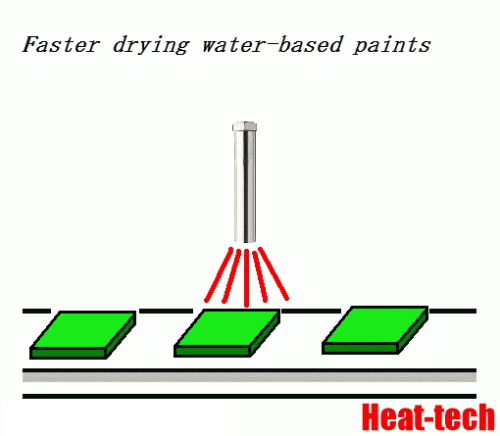
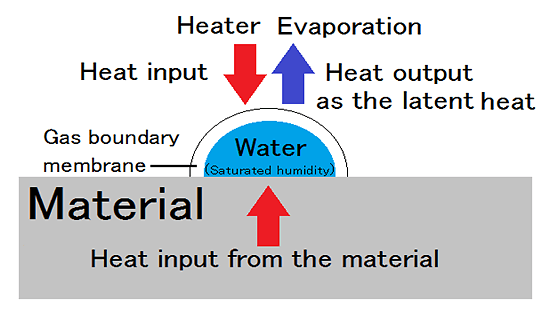
The drying time of surface adhesion water is determined by supply of evaporative latent heat.
The saturated vapor pressure of water and latent heat of evaporation
| Temp. | Pressure | latent heat | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ℃ | mmHg | kcal/kg | kJ/g |
| 0 | 4.6 | 597.1 | 2.502 |
| 1 | 4.9 | 596.6 | 2.500 |
| 2 | 5.3 | 596.0 | 2.498 |
| 3 | 5.7 | 595.4 | 2.495 |
| 4 | 6.1 | 594.9 | 2.493 |
| 5 | 6.5 | 594.3 | 2.491 |
| 6 | 7.0 | 593.8 | 2.488 |
| 7 | 7.5 | 593.2 | 2.486 |
| 8 | 8.0 | 592.6 | 2.483 |
| 9 | 8.6 | 592.1 | 2.481 |
| 10 | 9.2 | 591.5 | 2.478 |
| 11 | 9.8 | 590.9 | 2.475 |
| 12 | 10.5 | 590.4 | 2.473 |
| 13 | 11.2 | 589.8 | 2.471 |
| 14 | 12.0 | 589.3 | 2.469 |
| 15 | 12.8 | 588.7 | 2.466 |
| 16 | 13.6 | 588.1 | 2.464 |
| 17 | 14.5 | 587.5 | 2.461 |
| 18 | 15.5 | 587.0 | 2.459 |
| 19 | 16.5 | 586.4 | 2.456 |
| 20 | 17.5 | 585.9 | 2.454 |
| 21 | 18.6 | 585.3 | 2.452 |
| 22 | 19.8 | 584.8 | 2.450 |
| 23 | 21.1 | 584.2 | 2.447 |
| 24 | 22.4 | 583.6 | 2.445 |
| 25 | 23.8 | 583.1 | 2.443 |
| 26 | 25.2 | 582.5 | 2.440 |
| 27 | 26.7 | 581.9 | 2.438 |
| 28 | 28.3 | 581.4 | 2.436 |
| 29 | 30.0 | 580.8 | 2.433 |
| 30 | 31.8 | 580.2 | 2.431 |
| 31 | 33.7 | 579.7 | 2.428 |
| 32 | 35.7 | 579.1 | 2.426 |
| 33 | 37.7 | 578.5 | 2.423 |
| 34 | 39.9 | 578.0 | 2.421 |
| 35 | 42.2 | 577.4 | 2.419 |
| 36 | 44.6 | 576.8 | 2.416 |
| 37 | 47.1 | 576.2 | 2.414 |
| 38 | 49.7 | 575.7 | 2.412 |
| 39 | 52.4 | 575.1 | 2.409 |
| 40 | 55.3 | 574.5 | 2.407 |
| 41 | 58.3 | 574.0 | 2.405 |
| 42 | 61.5 | 573.4 | 2.402 |
| 43 | 64.8 | 572.8 | 2.400 |
| 44 | 68.3 | 572.2 | 2.397 |
| 45 | 71.9 | 571.7 | 2.395 |
| 46 | 75.7 | 571.1 | 2.392 |
| 47 | 79.6 | 570.5 | 2.390 |
| 48 | 83.7 | 570.0 | 2.388 |
| 49 | 88.0 | 569.4 | 2.385 |
| 50 | 92.5 | 568.8 | 2.383 |
| 51 | 97.2 | 568.2 | 2.380 |
| 52 | 102.1 | 567.6 | 2.378 |
| 53 | 107.2 | 567.1 | 2.376 |
| 54 | 112.5 | 566.5 | 2.373 |
| 55 | 118.1 | 565.9 | 2.371 |
| 56 | 123.9 | 565.3 | 2.368 |
| 57 | 129.9 | 564.7 | 2.366 |
| 58 | 136.1 | 564.1 | 2.363 |
| 59 | 142.7 | 563.6 | 2.361 |
| 60 | 149.4 | 563.0 | 2.359 |
| 61 | 156.5 | 562.4 | 2.356 |
| 62 | 163.8 | 561.8 | 2.354 |
| 63 | 171.5 | 561.2 | 2.351 |
| 64 | 179.4 | 560.6 | 2.349 |
| 65 | 187.6 | 560.0 | 2.346 |
| 66 | 196.2 | 559.5 | 2.344 |
| 67 | 205.0 | 558.9 | 2.341 |
| 68 | 214.3 | 558.3 | 2.339 |
| 69 | 223.8 | 557.7 | 2.336 |
| 70 | 233.8 | 557.1 | 2.334 |
| 71 | 244.1 | 556.5 | 2.331 |
| 72 | 254.7 | 555.9 | 2.329 |
| 73 | 265.8 | 555.3 | 2.326 |
| 74 | 277.3 | 554.7 | 2.324 |
| 75 | 289.2 | 554.1 | 2.321 |
| 76 | 301.5 | 553.5 | 2.319 |
| 77 | 314.2 | 552.9 | 2.316 |
| 78 | 327.4 | 552.3 | 2.314 |
| 79 | 341.1 | 551.7 | 2.311 |
| 80 | 355.3 | 551.1 | 2.309 |
| 81 | 369.9 | 550.5 | 2.306 |
| 82 | 385.0 | 549.9 | 2.304 |
| 83 | 400.7 | 549.3 | 2.301 |
| 84 | 416.9 | 548.7 | 2.299 |
| 85 | 433.6 | 548.1 | 2.296 |
| 86 | 450.9 | 547.5 | 2.294 |
| 87 | 468.7 | 546.9 | 2.291 |
| 88 | 487.2 | 546.2 | 2.288 |
| 89 | 506.2 | 545.6 | 2.286 |
| 90 | 525.9 | 545.0 | 2.283 |
| 91 | 546.2 | 544.4 | 2.281 |
| 92 | 567.1 | 543.8 | 2.278 |
| 93 | 588.7 | 543.2 | 2.276 |
| 94 | 611.0 | 542.6 | 2.273 |
| 95 | 634.0 | 541.9 | 2.270 |
| 96 | 657.7 | 541.4 | 2.268 |
| 97 | 682.1 | 540.7 | 2.265 |
| 98 | 707.3 | 540.1 | 2.263 |
| 99 | 733.3 | 539.4 | 2.260 |
| 100 | 760.0 | 538.8 | 2.257 |
| 101 | 787.0 | 538.1 | 2.254 |
| 102 | 815.2 | 537.4 | 2.251 |
| 103 | 844.2 | 536.8 | 2.249 |
| 104 | 874.5 | 536.2 | 2.246 |
| 105 | 906.1 | 535.6 | 2.244 |
| 106 | 938.4 | 535.0 | 2.241 |
| 107 | 971.6 | 534.3 | 2.239 |
| 108 | 1003.7 | 533.7 | 2.236 |
| 109 | 1040.0 | 533.0 | 2.233 |
| 110 | 1074.6 | 532.4 | 2.231 |
The quantity of heat which heated material becomes a constant drying period, while waterdrop is on the surface, since it is consumed as vapor-ized latent heat.
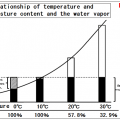
Although it can heated to the temperature which can untill withstand the material, as shown in the following table, there is only a difference of 10% to 100 ℃ from 0 ℃.
It seems that there is little necessity of raising material temperature by force.
<<Evaporation heat of the water 1g >>
| Temp.℃ | 0℃ | 20℃ | 40℃ | 60℃ | 80℃ | 100℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| latent heat | 2502J | 2454J | 2407J | 2359J | 2309J | 2257J |
The adhering water has been adhered by the interfacial tension on the material surface.
The vapor pressure of water adhering is equal to the saturated vapor pressure, and since the evaporation temperature of water is proportional to pressure, if low pressure and a vacuum are used, low-temperature drying will be made.
 HEAT-TECH Best Technology Online Shop
HEAT-TECH Best Technology Online Shop