INDEX
Basic principle
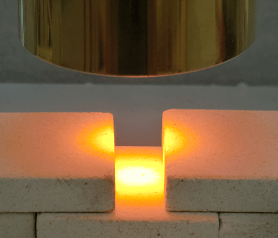
This figure shows the case where the object to be heated is small and equal to or smaller than the condensing diameter (width) of the halogen heater.
Make a groove in a simple way and place the object to be heated inside the groove.
The heating target of groove heating is heated with three elements.
1.Direct heating from heat source
2.Heating by reflected light from the wall
3.Heating by radiant heat on the wall
Preventing adverse effects of updraft
Open heating also heats the air around the object to be heated, causing the air to expand thermally and become lighter, creating an updraft.
Air at normal temperature and normal pressure flows into the space that has become lean and low pressure due to the updraft.
This flowing air comes into contact with the object to be heated and cools it down to room temperature, which is not good for heating work.
Frame heating does not generate a flow of cooling air, creating an effective heating environment.
Verification of high temperature heating method – Comparison of open heating and groove heating
If inert gas is flowed into the groove, oxidation-free or low-oxidation processing can be performed.
Covering the top of the groove with quartz glass will make it more perfect.
Comparison of open irradiation and groove heating
Taking HPH-60/f30/36v-450w with a focal length of 30 mm with a Φ60 condenser mirror as an example,
As the rated focal diameter is φ8, it is suitable for groove heating.
The time to reach 800℃ can be reached within 20 seconds with groove heating but not with 40 seconds with open heating.
Elongation at high temperature area is different when retroreflective heating light is used.