INDEX
1. Reduce the distance
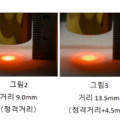
The closer the distance from the heater to the object to be heated, the higher the temperature it can be heated to.
Even in condensed heating, the shorter the condensed distance, the higher the temperature can be.
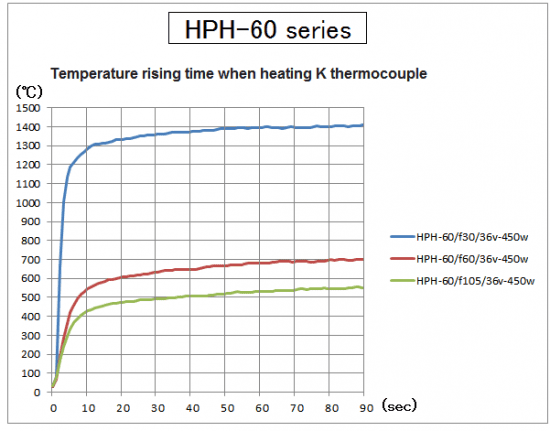
In the HPH-60 series of halogen point heaters,
Even with the same 450W in the order of f30>f60>f105, the temperature will rise if the distance is close.
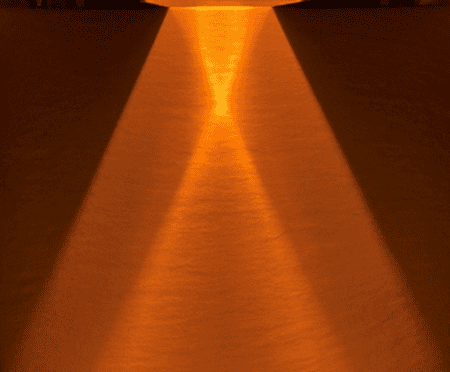
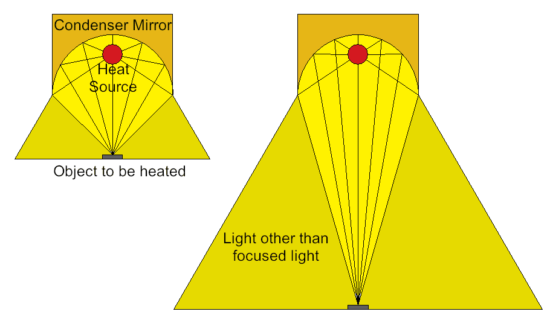
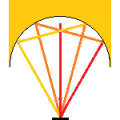
In condensed heating, the light from the heat source is focused, but the light is also scattered outside the focused range.
The photo below is a photo of a condensing halogen line heater.
Although the light is focused on a single point by a condensing mirror, the light is also scattered outside the focused area.
When light is diffused, it is attenuated. Therefore, the closer the distance, the better the heating efficiency.
This phenomenon is also observed in everyday life, where nearby light sources are brighter than distant ones.
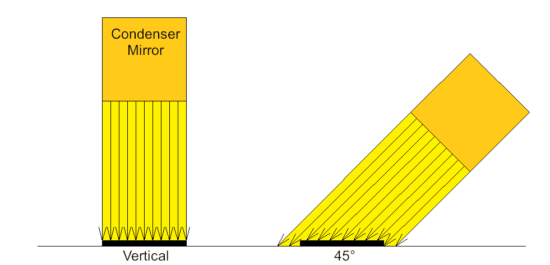
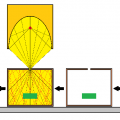
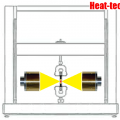
2.Irradiate at a vertical angle
When heating with a parallel light type condensing mirror, the distance between the centers is the same and the irradiation angle is diagonal, and the irradiation angle is vertical. The temperature of the object will be higher if the heating area is smaller.
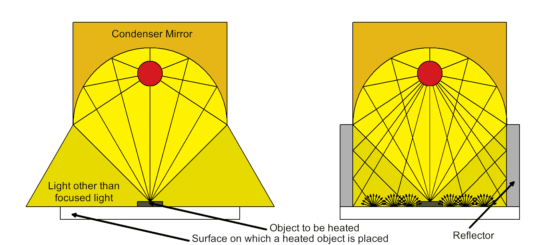
3.Use light that does not hit the object to be heated
A reflector is used to reflect the light that does not hit the object to be heated.
The reflective material uses a material with high reflectivity.
By doing so, you can additionally heat the “object to be heated” and “the surface on which a heated object is placed.”
The unabsorbed light is reflected again and contributes to the heating of the object being heated.
Also, since the object to be heated and the surface on which a heated object is placed are in contact,
A material with good infrared absorption and high thermal conductivity is used for the surface on which the heated object is placed.
The surface absorbs light and heats up, and if the surface becomes hotter, it can transfer heat to the object being heated.
This method works even if you don’t use a reflector.
 HEAT-TECH Best Technology Online Shop
HEAT-TECH Best Technology Online Shop