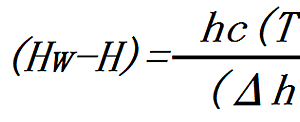Constant drying period is the mass of the water which evaporates per unit time and unit surface area. The unit is kg/s㎡. Constant drying rate Jc is expressed by the following equation. kH: Mass transfer coefficient Hw: Saturated absolute humidity ...
Read More »1-8.Why is the constant drying period. – Moisture movement in wet material.
Inside moisture material, movement of water (liquid) mainly takes place from the point that moisture content is high to a low point on the surface from an inside in accordance with a slope. There is capillary suction force action, osmotic ...
Read More »1-7.Drying characteristic curve – Relation between a drying rate and moisture content
The drying speed is taken along a vertical axis, average moisture content is taken along a horizontal axis and the above figure is described, it will become a dry characteristic curve. The drying speed is quantity of water evaporating in a ...
Read More »1-6.The Local moisture content and the Average moisture content
In general, the moisture content of the material is different in the center and the surface of the material. So, it called the Local moisture content, which is the moisture content of any measurement point. And, it called the Average ...
Read More »1-5.Equilibrium moisture content and Critical moisture content – Influence of temperature and relative humidity
The point which shifts to the Decreasing drying period from the Constant drying period is called the Critical moisture content Wc. The moisture content in which dryness does not advance any more is called the Equilibrium moisture content We. In ...
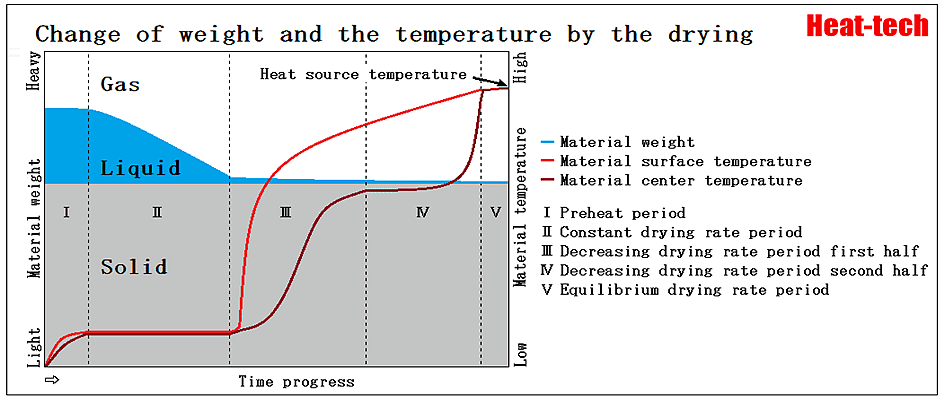
Read More »1-4.Change of weight and the temperature by the drying
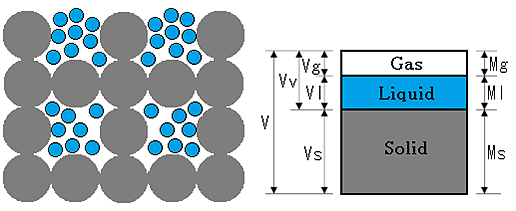
As shown in the figure above, wet material is made up the solid , the liquid and the gas as a gap. The weight of material is the sum total of the liquid and the solid. Since the solid weight ...
Read More »1-3.How to expressions the moisture in the material
As shown in the figure above, wet material is made up the solid , the liquid and the gas as a gap. Gas Mass : Mg Liquid Mass : Ml Solid Mass : Ms Gas volume : Vg Liquid volume ...
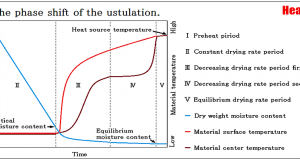
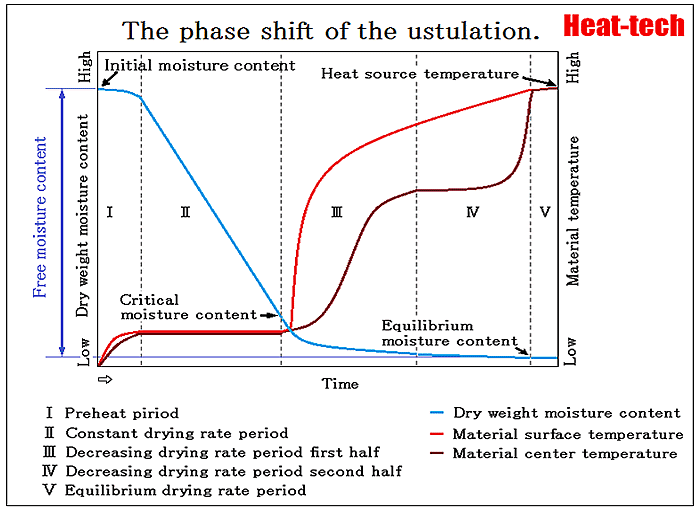
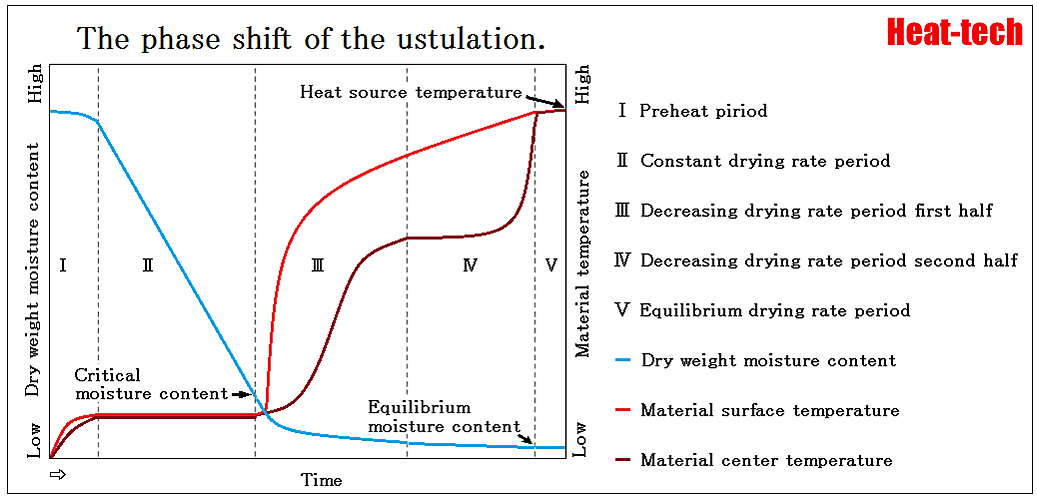
Read More »1-2.The phase shift of the ustulation
Ⅰ.Preheat piriod The material change from initial state to the state that fitted the dry condition. Ⅱ.Constant drying period The surface and the central temperature of materials are kept by the equivalence, and the period which water content decreases linearly ...
Read More »1-1.What is drying
The drying is the process of giving heat and a wind to the moist material containing liquids, a small amount of water and a solvent, evaporating a liquid, removing, and drying a product. As a typical example, in the process ...
Read More » HEAT-TECH Best Technology Online Shop
HEAT-TECH Best Technology Online Shop