[ Problem Point ]
To evaluate the safety of lithium-ion batteries, it was necessary to conduct tests to assess the risks of heat generation, expansion, and ignition at specific temperatures. However, conventional methods that heated the entire battery made it difficult to detect localized anomalies.
[ ⇒Kaizen Point ]
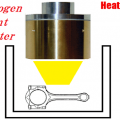
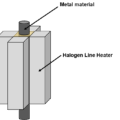
By using the halogen point heater, it became possible to heat only specific areas of the battery cell, allowing for a detailed analysis of localized anomaly mechanisms. Additionally, the heater’s temperature control function made it easier to conduct tests under multiple temperature conditions.
 HEAT-TECH Best Technology Online Shop
HEAT-TECH Best Technology Online Shop