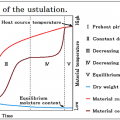
As for the Drying characteristic curve of the Decreasing drying rate period, five patterns appear with the characteristic of material.
The type of material
The composition of material
The shape of material
The possession state of water
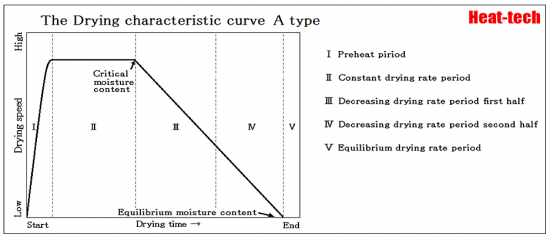
A-Type
A-type is the velocity curve seen in the material with a capillary water.
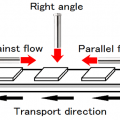
Non-hydrophilic property grain powder material layer, a molding material less than 5mm diameter, powder material and droplets were dispersed into hot air is distributed, or, it will appear when it is agitated.
Drying time tends to be proportional to the size of material.
When the Decreasing drying rate curve can approximate in a straight line, it can express by the following formulas.
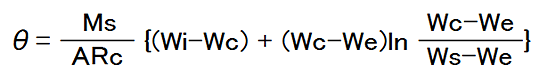
θ: drying time
Ms: material mass
A : drying area
Rc: constant drying rate
Wi: initial moisture content
Ws: target moisture content
Wc: critical moisture content
We: equilibrium moisture content
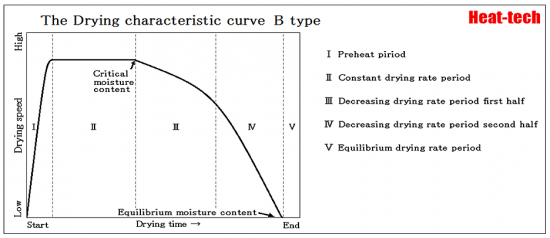
B-type
B-type is the velocity curve seen in the material with a capillary water.
Non-hydrophilic property grain powder material layer, fibrous material layer, fine particulate material layer,
In the molding material less than 5mm diameter, it appear in the vacuum drying and heating steam drying.
Drying time tends to be proportional to the thickness of material.
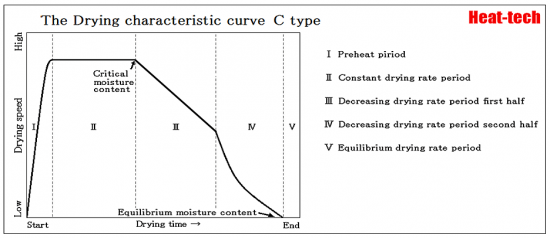
C-type
It appears into material with osmotic water like clay, fine ceramics, and wood.
Drying time tends to be proportional to the thickness of material.
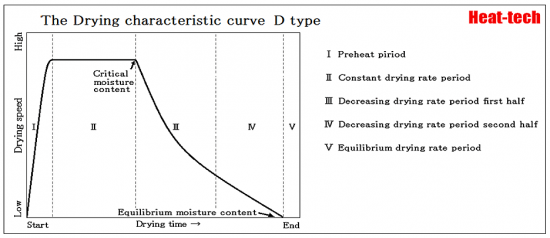
D-type
It appears in molding material and sedimentary layers.
Drying time tends to be proportional to the thickness of material.
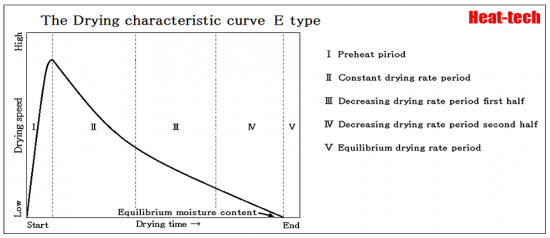
E-type
It appears into homogeneous material (moisture diffusion material) like soap, a polymer solution, and gelatin.
Drying time tends to be proportional to the square of material thickness.
 HEAT-TECH Best Technology Online Shop
HEAT-TECH Best Technology Online Shop