INDEX
■ What is heat/cool control?
For example, when conducting a performance evaluation test for electronic equipment, it is necessary to control the heater and cooling mechanism simultaneously.
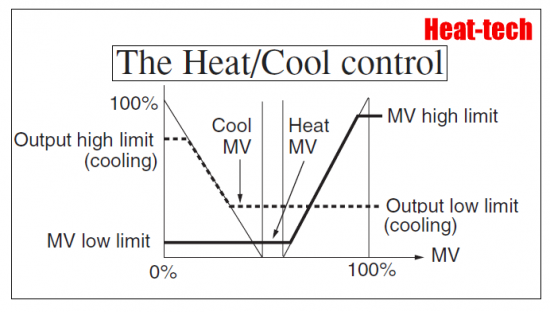
Heating / cooling control refers to a method in which one controller operates and controls two outputs, heating output and cooling output.
In a temperature controller that can select general heating / cooling control operation, the heating side operates in “reverse operation” and the cooling side operates in “normal operation”.
Reverse action: Control action in which the output of the controller decreases when the temperature measurement value increases.
(Temperature rises → heating output decreases)
Direct action: Control action in which the controller output increases when the temperature measurement value increases.
(Temperature rises → cooling output increases)
■ PID setting for heat/cool control
Devices that require heating / cooling control have two control systems, a heating control system (heater to temperature sensor) and a cooling control system (cooling mechanism to temperature sensor). In most cases, the response characteristics of the heating system and cooling system Is different.
For this reason, the controller is also made so that the PID constant can be set for each of the heating system and the cooling system.
■ Setting method of heat/cool PID constant
There are two types of PID constant setting methods for heating / cooling control. Which method differs depending on the controller model, grade, and controller manufacturer.
(1) Only the proportional band can be set differently for heating and cooling
Only the proportional band setting can be set individually for the heating system and the cooling system as “heating proportional band” and “cooling proportional band”. “Integration time setting” and “derivative time setting” are common setting values for heating and cooling. Is used.
Therefore, as a heating / cooling PID controller, the control calculation is performed using four PID parameters of “heating proportional band”, “cooling proportional band”, “integration time” and “derivative time”.
In the case of this PID constant setting method, the adjustment itself is not so difficult because there is only one increase in setting items, but on the other hand, it is restricted from the viewpoint of precise adjustment.
(2) Independent type PID constant setting for heating control system and cooling control system
Independent PID constants can be set for each of heating and cooling, allowing more precise adjustment of constants, but it is difficult to optimize PID constants accordingly.
■ Features of heating and cooling operation
(1) With respect to the set temperature, the output value on the heating side is output in the area where the temperature measurement value is low, and the output value on the cooling side in the area where the temperature measurement value is high.
(2) A dead band can be provided at the switching point between the heating output and the cooling output.
(3) Heating output and cooling output can be output by overlapping.
■ Application of heat/cool operation
Liquid crystal panel: heating / gas / cooling / gas
Printing machine rollers: heating / electric heater / cooling / water
Organic synthesis: heating / electric heater / cooling / water
Continuous reheating furnace: heating / gas / cooling / water
Formation of novel composite gel of egg white protein and polysaccharide: heating / electric heater / cooling / water
Injection machine: heating / electric heater / cooling / water
Food processing machinery: heating / electric heater / cooling / water
Water temperature management of live fish farming water tank equipment: heating / electric heater / cooling / water
Sake “Moromi (Unrefined sake”” manufacturing process: heating / electric heater / cooling / water
Plastic molding press: Heating / electric heater / cooling / water
Soy milk: heating / steam / cooling / water
Deep pressing of metal press cylinder: heating / electric heater / cooling / oil
Others: Reaction, polymerization, crystallization, dissolution, molding, and condensation processes in the chemical, pharmaceutical, rubber, and textile industries.
 HEAT-TECH Best Technology Online Shop
HEAT-TECH Best Technology Online Shop