Name of engineer plastics, DuPont was the first time used in the PR of the product name of the polyacetal resin “Delrin” in 1959.
Since this resin is used in mechanical parts such as gears, it was given the designation of “Engineers plastics” = industrial plastics.
General-purpose resin, Engineering plastics and Super engineering plastics, has been distinguished by the deflection temperature under load (DTUL) as a measure of the heat resistance.
DTUL 100 ℃ or more have been regarded as Engineering plastics.
DTUL 150 ℃ or more have been regarded as Super engineering plastics.
General nature, DTUL 100 ℃ or more, strength less than 500kgf / cm2, flexural modulus less than 24000kg / cm2.
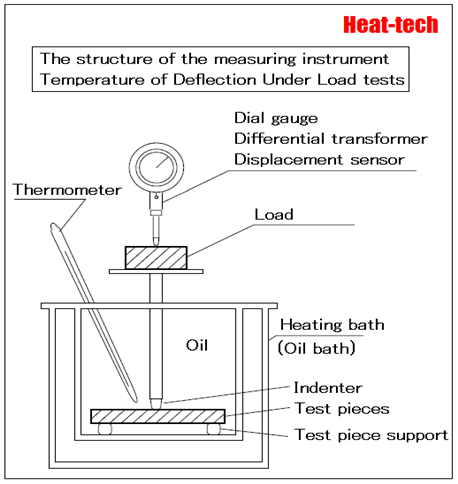
Deflection temperature under load (DTUL)
Deflection temperature under load, is also known as one the thermal deformation temperature of the test method to evaluate the heat resistance of the synthetic resin.
In a state of applying a load which is determined in the test method standard, gradually raising the temperature of the sample is the temperature at which the magnitude of the deflection is constant value.
Test method has been defined in ASTM D648.
In addition a constant load to the test piece, when the temperature was increased at 2 ℃ / min to find the temperature at which the displacement becomes constant value.
Flexural modulus is the temperature at which 2,514 kgf / cm2 = 0.25 GPa or 10,000 kgf / cm2 = 1GPa.
The characteristics of the temperature change of the elastic modulus of the resin, since the rapid elastic modulus is lowered when it exceeds the glass transition temperature, deflection temperature under load might be temperature values close to the glass transition temperature.
Engineering plastics, depending on the presence or absence of the crystal structure, it can be divided into the non-crystalline resin and the crystalline resin.
Because many of the properties are improved by incorporating reinforcing fibers and other fillers, in fact there is a difference in characteristics for each grade in various resins.
To actually use, you will need to make sure that in the catalog of each manufacturer.
Non-crystalline resin name
Transparency, poor solvent resistance, toning easy, bad flow, wear relatively large, sliding property slightly inferior, flexible, tough, it is difficult to crack, sleigh small, shrinkage small
1. Polycarbonate (PC)
Transparent resin. Low mold shrinkage rate, a small dimensional stability good water absorption. Impact resistance, creep resistance, electrical characteristics are also very good. Is inferior in chemical resistance, it must be careful to stress cracking. Because it has an ester bond in the molecule, the physical properties undergo a when hydrolyzed do not pre-dried drops prior to molding. Recently, the use of organic halogen-based flame retardants from fear of dioxin, was not be able to receive approval in the eco-label such as Germany. Therefore, and non-halogen flame retardant treatment is considered, already phosphorus flame retardant grade, silicone-based flame retardant grades have been developed. In addition, since it is flame retardant by the ABS of non-halogen difficult, has begun ABS alternative by flame retardant alloy grades such as PC / ABS and PC / HIPS.
2. Modified polyphenylene ether (mPPE)
Stiffness, impact resistance, and is stable at a wide temperature range fatigue resistance. Low mold shrinkage, and excellent dimensional stability. Low specific gravity, low water absorption, it is excellent in hot water resistance. Chemical resistance acids are not damaged by alkalis, aromatic hydrocarbons, the halogenated hydrocarbons are eroded. While juice out during molding of the flame-retardant grade is a problem, recently it has been improved by the high molecular weight flame retardant. Originally inferior in weather resistance (yellowing) is, light resistance of the flame retardant grade close to the ABS has recently been developed. General for possible from and flame retardancy rating ULHB using phosphorus-based flame retardant to V-0, problems such as dioxin is not a concern.
Crystalline resin name
Opacity, heat resistance high, excellent solvent resistance, flow better, it is suitable for thin-wall molding, abrasion wear resistance and sliding properties good, high rigidity, high hardness, brittle and fragile, easy to warp and shrinkage greater
1. Polyamide (PA)
Nylon it also called. A variety due to the difference in chemical structure. It is particularly excellent in impact resistance. Abrasion and wear resistance, (except strong acid, phenol) chemical resistance, oil resistance, and excellent gas barrier properties. On the chemical structure, because of the high water absorption, stiffness degradation, it must be careful to dimensional changes. However, improvements and by the alloy of PPE in recent years, there is a development trend such as low water absorption (aromatic nylon) by filler.
2. Polyacetal (POM)
It has excellent fatigue resistance. Abrasion and wear resistance, low noise property, chemical resistance, creep resistance, a very balanced good resin excellent in dimensional stability. Water absorption less. However, it is not a serious problem in the compact moldings, sink marks are conspicuous in thick molded article, deformation is liable to occur in the large molded article. Because it contains a lot of oxygen in the molecule, the flame retardant is difficult. Originally, it is inferior in weatherability, enhanced grade weather resistance have been developed by the selection of UV stabilizers and pigments recently.
3. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT)
Tough, high rigidity, heat resistance, heat aging resistance, electrical properties, weather resistance, chemical resistance, dimensional stability, and I is excellent in moldability. Because it has an ester bond in the molecule, the physical properties undergo a when hydrolyzed do not pre-dried drops prior to molding. Flame retardant is but easy, current situation, in many cases the bromine-based flame retardant is used, consideration of load reduction on the environment is expected. Recently, and increasing the heat cycle resistance of the metal insert molding, low warpage, etc., grades having improved low gasification flame retardant PBT have been developed.
4. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
Heat resistance, chemical resistance, electrical properties, and excellent weather resistance. Because it has an ester bond in the molecule, the physical properties undergo a when hydrolyzed do not pre-dried drops prior to molding. Low temperature of the mold temperature, is expected to have excellent melting heat stability.
Thermal properties of the Engineering plastics (typical)
| Non-crystalline resin name | Symbol | Density [g/cm3] | Specific heat [J/g ℃] | Thermal conductivity [W/m K] | Heat distortion temp. ℃ | GF reinforced DTUL ℃ | Tg ℃ | Tm ℃ | Molding temp. ℃ | Mold temp. ℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polycarbonates | PC | 1.2 | 1.26 | 0.19 | 135 | 146 | 145-150 | 250 | 250-320 | 70-120 |
| modified-Polyphenyleneether | mPPE | 1.06 | 1.95 | 0.15 | 107-149 | 142 | 211 | 300 | 230-350 | 70-120 |
| Crystalline resin name | Symbol | Density [g/cm3] | Specific heat [J/g ℃] | Thermal conductivity [W/m K] | Heat distortion temp. ℃ | GF reinforced DTUL ℃ | Tg ℃ | Tm ℃ | Molding temp. ℃ | Mold temp. ℃ |
| Polyamides/Nylon 6 | PA6 | 1.14 | 1.59 | 0.25 | 63 | 190 | 48-50 | 225 | 230-290 | 60-100 |
| Polyamides/Nylon 6-6 | PA66 | 1.14 | 1.42 | 0.24 | 70 | 240 | 50 | 265 | 250-300 | 60-100 |
| Polyoxymethylene plastic | POM | 1.41 | 1.47 | 0.23 | 110-130 | 163 | -56 | 167-178 | 175-210 | 60-100 |
| Polybutylene terephthalate | PBT | 1.52-1.67 | 1.67-1.76 | 0.22 | 60 | 217 | 22 | 224 | 230-270 | 70-120 |
| Polyethylene terephthalate | PET | 1.47-1.67 | 1.26 | 0.31 | 240 | 235 | 69 | 260 | 265-280 | 80-120 |
Tg:Glass transition point
Tm:Melting point
 HEAT-TECH Best Technology Online Shop
HEAT-TECH Best Technology Online Shop