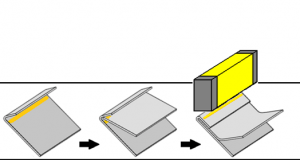
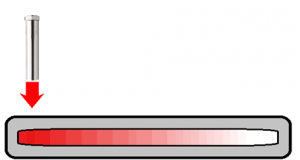
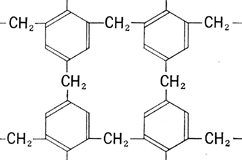
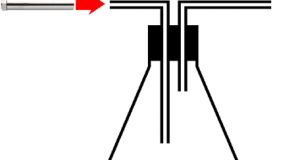
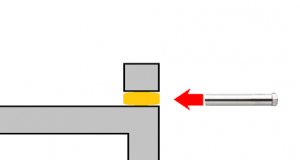
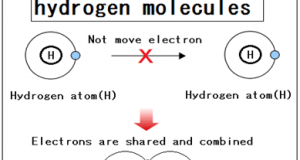
컴팩트한 설비이므로, 유지비가 염가로 2차 처리가 불필요하고, 공정의 간소화, 시간 단축, 경비 절감 모든 균종에 유효합니다 내구균을 만들지 않습니다 상온으로 살균할 수 있습니다 대상물을 변질시킬 걱정이 없습니다 << 자외선 살균의 메리트 >> 썬탠 등, 자외선에 의한 변화나 작용은 옛부터 알려져 있었습니다만, ...
Read More »자외선 램프 가격표
자외선 선형 조사기 Lab-kit 형식 비고 가격 JPY 자외선 점형 조사기 Lab-kit LKUVP-30 + UVPC 전원・설치대 부속 ¥274,000 자외선 점형 조사기 Lab-kit LKUVP-60 + UVPC 전원・설치대 부속 ¥349,000 자외선 선형 조사기 Lab-kit LKUVL-115 전원・설치대 부속 ¥125,000 자외선 점형 조사기 UVP-30 ...
Read More »제 49 호 핫멜트의 가열 건조
[ 문제점 ] 핫멜트의 건조 시간을 단축 할 필요가 있었다 [ 개선의 포인트 ] 선 집광 형 할로겐 라인 히터를 사용했다. 선 집광 형이므로, 핫멜트의 도포 위치에 맞게 정확하게 가열 할 수 있고, 건조 시간을 단축 할 수 있었다. 라인의 ...
Read More »3 수지의 종류 -5 슈퍼 엔지니어링 플라스틱Super engineering plastics
슈퍼 엔지니어링 플라스틱 (이하 SEP로 약칭)는 엔지니어 플라스틱의 기능을 강화한 수지입니다. 일부에서는 “특수 엔지니어링 플라스틱 ‘라고도합니다. SEP는 열에 약하다는 플라스틱의 본질적인 특성을 개선 한 내열성이 높은 제 3 세대 합성수지입니다. 고 내열성 의해 가동부에서 마찰 열성 향상으로 종합적인 기계적 강도도 ...
Read More »제 28 호 수지 보스 적외선 열 코킹
[ 문제점 ] 펀치에 수지가 부착 가공 불량의 원인이되고 있었다. [ 개선의 포인트 ] 할로겐 포인트 히터를 사용하여 수지 보스를 가열했다. 펀치를 사용하지 않는 공법이므로 문제가 해소했다. 섬유를 분리하지 않고 돔을 형성하기 때문에 기계적 강도가 향상되었다. 또한, 작업도 가볍게 가열되므로 ...
Read More »할로겐 히터 용 수동 전원 컨트롤러 HCV 시리즈
컬러 유니버설 디자인 형 HCV-CUD / HCVD-CUD 파란색 표시등을 채용하여 누구나보기 쉬운 배색했습니다. 주문 형식으로 CUD를 추가 지정하십시오. 표준형 HCV 볼륨을 탑재 해, 할로겐 히터 수동 전압 제어가 가능합니다. 냉각 용 DC 전원 탑재형 HCVD 볼륨 및 냉각 팬 전원을 탑재하고 공냉식 ...
Read More »3 수지의 종류 -4 엔지니어링 플라스틱 (Engineering plastics)
엔지니어 플라스틱의 이름은 1959 년에 미국 듀폰 사가 폴리 아세탈 수지의 제품명 ‘델린」의 PR에서 처음 사용했습니다.이 수지가 기어 등의 기계 부품에 사용에서 “엔지니어 플라스틱”= 산업용 플라스틱이라는 호칭을 부여했습니다. 범용 수지와 엔지니어 플라스틱과 슈퍼 엔지니어링 플라스틱은 내열성을 나타내는 척도로서 하중 굴곡 ...
Read More »제 27 호 약용주걱 (薬匙)의 고온 광 살균
[ 문제점 ] 지금까지 바탕 화면에 쉽게 고온 살균 할 수있는 것이 없었다. [ 개선의 포인트 ] 할로겐 포인트 히터를 사용했기 때문에 쉽게 고온 살균 수 있었다. 전력은 실험실 콘센트에서 쉽게 급전 할 수 있었다. 전기 광 살균이므로 약액의 보충 ...
Read More »3 수지의 종류 -3 열가소성 수지
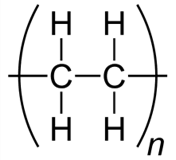
열가소성 수지는 일차원 구조 (선형 구조의 고분자의 집합)의 고체 고분자로 가열하면 용해하고 냉각하면 고체가됩니다. 유리 전이 온도 또는 융점까지 가열하여 말랑 말랑 해져서 원하는 형태로 성형 할 수있는 수지입니다.일반적으로 열가소성 수지는 절삭 · 연삭 등의 기계 가공이 어려운 경우가 많고, ...
Read More »제 100 호 히트 파이프의 차온 검사
[ 문제점 ] 조작성이 좋은 난방 장비가 필요했다. [ 개선의 포인트 ] 열풍 히터를 사용하여 히트 파이프를 가열했다.지금까지 할 수 없었던 다점 계측이 가능하게되었다.게다가 비접촉 가열이므로 제품의 품위가 향상되었다.
Read More »3 수지의 종류 -2 열경화성 수지
열경화성 수지는 열경화성 플라스틱이라고도 불리는 고분자 물질입니다.원료를 가열 · 가압하여 유동하고 제품의 형상입니다.구성하는 단량체 (모노머)의 결합이 삼차원의 입체적인 그물 구조를 가진 것으로, 입체 폴리머 또는 가교 폴리머라고도합니다.삼차원 입체 구조로 완성 된 것은 가열해도 더 이상 액체는 반환되지 않습니다.이것은 화학 반응하여 ...
Read More »제 99 호 혐기성 미생물의 배양
[ 문제점 ] 다미가스을 자유롭게 온도 변화시킬 수 없었다. [ 개선의 포인트 ] 내 환경 용 열풍 히터 DGH 시리즈를 사용하여다미가스을 자유롭게 온도 변화시켜 혐기성 미생물의 배양 시험을 실시했다.참신한 데이터가 많이 잡히고 연구가 진행되었다.
Read More »제 98 호 접착제 도장 건조
[ 문제점 ] 접착 밀봉 공정의 택트 타임의 단축이 요구되고 있었다. [ 개선의 포인트 ] 열풍 히터를 사용하여 씰을 건조했다.온도와 풍압의 이중 효과로 건조 시간이 짧아졌다.
Read More »3 수지의 종류 -1 결합과 분자의 형태
원자 집합 해 분자를 만듭니다.분자와 분자간에는 “분자간 력 ‘이라는 힘이 작용 고체화 (결정화)합니다.화학 결합은 원자가 안정을 추구 閉殻 구조를 획득하게 반응이며, 이러한 이유로 원자는 분자와 결정 등을 만들어 존재하고있는 것입니다.수지는 주로 다음과 같은 4 개의 결합이 있습니다. 1.공유 결합 공유 ...
Read More »알루미늄 와이어 가열 용해
할로겐 포인트 히터에서 알루미늄 와이어 가열 용해하는 데모입니다. 자세한 내용은 아래 사이트에서 확인하십시오.
Read More »수지 가열의 기초 지식 2 수지의 역사 -3 연표
앙리 부라코노 (Henri Braconnot 1780 년 5 월 29 일 – 1855 년 1 월 15 일 프랑스 화학자) 1832 앙리 부라코노 Henri Braconnot 니트로 셀룰로오스의 발견 전분이나면 등을 질산에 넣어 따뜻하게 녹인 물로하면 강도 성 백색 가루 니트로 셀룰로오스를 ...
Read More »온도 조절기 탑재 히터 컨트롤러
[주의] HCA 시리즈는 할로겐 히터를 제어 할 수 없습니다. 할로겐 히터의 제어는 HCV 시리즈, HHC2 시리즈, SSC 시리즈를 추천합니다. 과열 제로 설정하여 안정된 가열을 제공합니다. ※ HCA는 AT2 (안정적)로 초기 설정되어 있습니다. 사양 옵션 표준형 HCA 주 전원 스위치 히터 ...
Read More »수지 가열의 기초 지식 2 수지의 역사 -2 합성 수지의 발명
최초의 합성 수지 역사상 처음으로 공업화 된 합성 수지의 셀룰로이드는 상아로 만든 당구 공의 대체 재료로서 탄생했습니다. 코끼리 1 마리의 상아에서 8 개보다 많은 양의 당구 공을 제작 할 수 없었던 것으로 알려져 있습니다.1800 년대 중반에는 당구 공에 사용하는 상아 ...
Read More »할로겐 포인트 히터 HPH-35에 의한 솔더의 가열
이 비디오는 할로겐 포인트 히터 HPH-35의 초점 지름을 확인하는 데모입니다. 자세한 내용은 아래 사이트에서 확인하십시오.
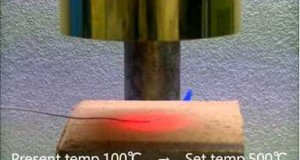
Read More »할로겐 포인트 히터 HPH-120의 PID오토 튜닝의 실례
이 비디오는 할로겐 포인트 히터 HPH-120의 오토 튜닝의 실례을 확인하는 데모입니다. 자세한 내용은 아래 사이트에서 확인하십시오.
Read More »Heat-tech News Letter –한국어판 – Vol. 009
■□■━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━■ □■ Heat-tech News Letter – Vol. 009 2015-07-15 ■━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━■□■ □ INDEX ■1.신제품의 안내합니다. ■2.새용도의 안내합니다. ■3.비디오 라이브러리 ■4.서포트 정보입니다. ■5.편집 후기 ┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓ ■1.신제품의 안내합니다. ┗━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┛ 1-1) 《 드럼통 액면계 내열 100 ℃ 형 》 DLC-100/+F시리즈 신제품 >>> https://heater.heat-tech.biz/ko/drum-level-communicator/product-drum-level-communicator/2365.html ...
Read More »수지 가열의 기초 지식 2 수지의 역사 -1 고분자와 수지·플라스틱
합성 수지 옛날에는 수지樹脂는 말 그대로 ‘나무樹의 “지방”(=脂)’, 즉 소나무 야니 나 옻칠 등과 같이 수액이 굳어진 것을 의미했습니다. 영어 resin도 독일어 harz도 “소나무 야니 ‘의 의미가 원래의 의미에서 사람이 만든 합성 수지의 경우 (synthetic resin)로 표기되어 있습니다. 1881 년에 ...
Read More »할로겐 폰트 히터 HPH-160/f40의 초점 거리와 초점 지름
이 비디오는 할로겐 포인트 히터 HPH-160/f40의 초점 지름을 확인하는 데모입니다. 자세한 내용은 아래 사이트에서 확인하십시오.
Read More »1.참고 문헌 – 수지 가열의 기초 지식
참고 문헌은 모두 일본에서 출판 된 저작물입니다. 따라서, 일본어로 표기합니다. 高分子のはなし / 功刀滋著 /三共出版/2014 ナノテク材料 : ポリマーナノコンポジット絶縁材料の世界 / 先端複合ポリマーナノコンポジット誘電体の応用技術調査専門委員会編 /電気学会/オーム社 (発売)/2014 トコトンやさしいプラスチック成形の本 / 横田明著 /日刊工業新聞社/2014//B&Tブックス/今日からモノ知りシリーズ プラスチックハードコート材料の最新技術 / 矢澤哲夫監修 /普及版/シーエムシー出版/2014//CMCテクニカルライブラリー:523/新材料・新素材シリーズ 生物とコラボする : バイオプラスチックの未来 / 工藤律子著 /岩波書店/2013//岩波ジュニア新書:759 プラスチックスの上昇と下降、そしてメロンの理力(メジャー・フォース) : 中西俊夫自伝 / 中西俊夫著 ...
Read More »목차 – 수지 가열의 기초 지식
이 세미나에서는 수지 가열 구조를 알기 쉽게 설명하는 것을 목적으로하고 있습니다. 1.참고 문헌 2.수지의 역사-1 고분자와 수지·플라스틱 2.수지의 역사-2 합성 수지의 발명 2.수지의 역사-3 연표 3.수지의 종류-1 결합과 분자의 형태 3.수지의 종류-2 열경화성 수지 3.수지의 종류-3 열가소성 수지 3.수지의 종류-4 엔지니어링 플라스틱 Engineering plastics 3.수지의 종류-5 슈퍼 엔지니어링 ...
Read More » HEAT-TECH 최선의 기술 온라인(on-line) 샵
HEAT-TECH 최선의 기술 온라인(on-line) 샵