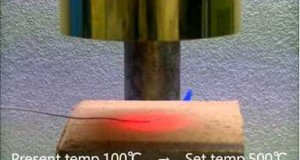
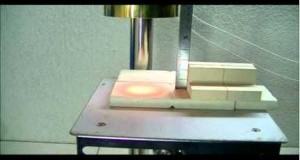
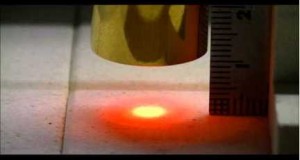
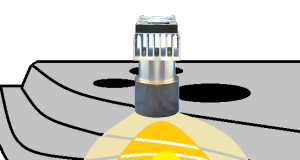
這部影片是一個演示確認 鹵素燈點加熱器HPH-120的自動調諧的實例。
Read More »鹵素燈點加熱器HPH-160/f40的 焦距和焦點直徑
這部影片是一個演示確認 鹵素燈點加熱器HPH-160/f40的焦點直徑。
Read More »鹵素燈點加熱器HPH-120/f45的 焦距和焦點直徑
這部影片是一個演示確認 鹵素燈點加熱器HPH-120/f45的焦點直徑。
Read More »鹵素燈點加熱器HPH-60/f60的 焦距和焦點直徑
這部影片是一個演示確認 鹵素燈點加熱器HPH-60/f60的焦點直徑。
Read More »鹵素燈點加熱器HPH-60/f30的 焦距和焦點直徑
這部影片是一個演示確認 鹵素燈點加熱器HPH-60/f30的焦點直徑。
Read More »鹵素燈點加熱器HPH-35的 焦距和焦點直徑
這部影片是一個演示確認 鹵素燈點加熱器HPH-35的焦點直徑。
Read More »鹵素燈點加熱器HPH-18的 焦距和焦點直徑
這部影片是一個演示確認 鹵素燈點加熱器HPH-18的焦點直徑。
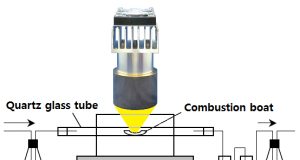
Read More »第26號 焚燒廢棄物中的金屬分析
《 問題點 》 迄今為止能作為台上的高溫加熱的誰也不簡單地有。 《 ⇒改善的要點 ...
Read More »木的加熱 系列7-輕木(Balsa)的加熱
這個視頻是用鹵素燈點加熱器 加熱輕木(Balsa) 的公開表演。
Read More »第25號 早期硬化密封劑應用程序之後的乾燥
《 問題點 》 器材根據高頻熱大了以及版面設計變化困難了。 《 ⇒改善的要點 》 ...
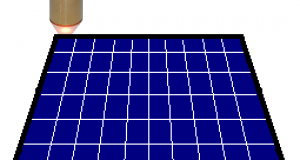
Read More »第24號 太陽能電池板的精密檢查
《 問題點 》 希望提高高品質的發電效率。 《 ⇒改善的要點 》 它能夠測試太陽 ...
Read More »木的加熱 系列6-Sengon勞特(南洋楹)的加熱
這個視頻是用鹵素燈點加熱器 加熱Sengon勞特(南洋楹)的公開表演。
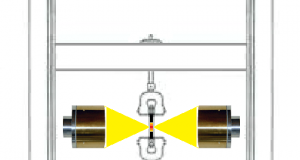
Read More »第23號 拉伸試驗機的溫度設定(非磁性材料·高溫素材)
《 問題點 》 需要將非磁性材料加熱到高溫的設備。 《 ⇒改善的要點 》 使用鹵 ...
Read More »木的加熱 系列5-貝殼杉的加熱
這個視頻是用鹵素燈點加熱器 加熱貝殼杉 的公開表演。
Read More »木的加熱 系列4-桐的加熱
這個視頻是用鹵素燈點加熱器 加熱桐 的公開表演。
Read More »木的加熱 系列3-桧的加熱
這個視頻是用鹵素燈點加熱器 加熱柏 的公開表演。
Read More »木的加熱 系列2-杉的加熱
這個視頻是用鹵素燈點加熱器 加熱杉 的公開表演。
Read More »5-4.正確使用近紅外加熱和遠紅外加熱
鹵素燈加熱器用於近紅外線的輻射加熱。在約 3000℃ 從加熱元件輻射的電磁波中, ...
Read More »木的加熱 系列1-日本雪松的加熱
這個視頻是用鹵素燈點加熱器 加熱日本雪松 的公開表演。
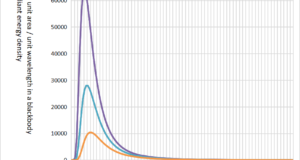
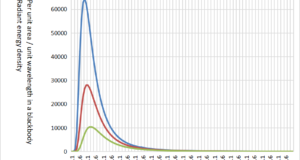
Read More »5-3.關於熱輻射的波長
絕對溫度為 0K(開爾文)或更高的物體會以電磁波的形式輻射與物體溫度相對應的波長 ...
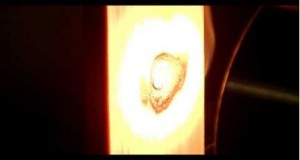
Read More »鋅的溶解,用鹵素燈點加熱器
這個視頻是 鋅的溶解,用鹵素燈點加熱器的示威。
Read More »5-2.關於反射的類型
反射有兩種主要類型。 鏡面反射(法線反射) 鏡面反射(規則反射)是指保持“反射定 ...
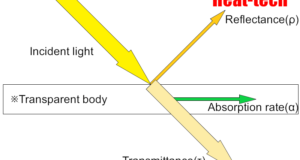
Read More »5-1.光反射率、透射率、吸收率=發射率
每種物質都由非常小的顆粒組成。構成該物質的分子根據溫度具有不同的分子運動。分子由 ...
Read More »4-1.直至鹵素燈的發展歷程
碳絲的發展 鹵素燈是從白熾燈泡演變而來的。碳纖維用於早期發熱燈泡的燈絲。鋨和鉭等 ...
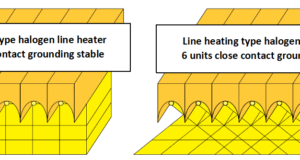
Read More »3-8.使用線加熱型鹵素燈線型加熱器進行廣泛的表面加熱
通過排列多種線材加熱類型,將焦距與額定距離分開,可以加寬焦距,進行大範圍的加熱。 ...
Read More » HEAT-TECH 最佳技術網店
HEAT-TECH 最佳技術網店