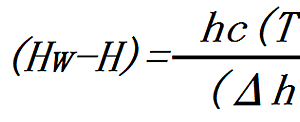[ Problem Point ] In the winter, it is in trouble sealant without drying out. [ ⇒Kaizen Point ] Dry by heating with a Halogen Point Heater. Easy dried.
Read More »10. The main materials Specific gravity,specific heat and thermal conductivity
Thermal properties of various substances Material-Metal Reference temperature [℃] Density [g/cm3] Specific heat [J/g ℃] Thermal conductivity [W/m K] Zinc 20 7.13 0.383 113 Aluminum 20 2.7 0.9 204 Aluminum oxide 20 3.9 0.875 30 Duralumin 20 2.79 0.84 164 ...
Read More »2-2.There is a limit to the water vapor contained in the air
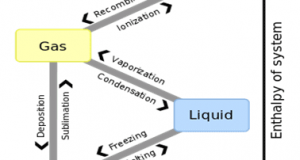
There is a limit to the amount of water vapor that air can contain. Within the air, water movement may become gas (vapor) from a liquid, that or become liquid from gas (vapor) has been constantly repeated. The temperature that ...
Read More »9. Attention in the infrared rays use (Q&A)
(Q) Can heat in the far-infrared rays metal? (A) Since there is a lot of metal electrons, it reflects the electromagnetic waves (far-infrared rays) in general. The good conductivity metal such as gold and aluminum, it is hard to heating ...
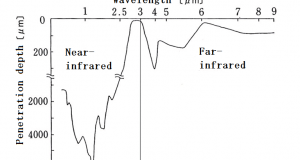
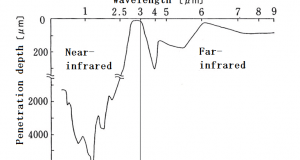
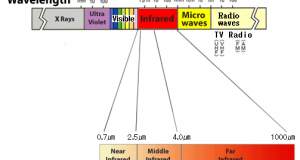
Read More »8. Comparison of far-infrared rays and near-infrared rays
(1) Infrared Rays are subdivided into several scheme. ISO 20473 specifies the following scheme: Designation Abbreviation Wavelength Near-Infrared NIR 0.78–3 µm Mid-Infrared MIR 3–50 µm Far-Infrared FIR 50–1000 µm (2) Difference in frequency = The difference between the heating capacity By “Wien’s displacement ...
Read More »7. Generation of far-infrared rays
The method of heating the ceramic to make a far-infrared artificially is common. The fine ceramics of an alumina system or a zirconium system are used well. Wavelength and the emittance change by a kind and the heating temperature of ...
Read More »2-1.What is the humidity?
The Chapter 1 focused on moisture inside material. The Chapter 2 focuses on the moisture emitted in the form of vapor into the air. Definition of the humidity Of humidity, it is a representation of a number the wetness in ...
Read More »6. Absorption rate of infrared rays
【 Infrared Absorption Rate 】 Please confirm the index of absorption of infrared rays in this table. The material absorbed by about 0.5 = 50% or more is suitable for the infrared heating.
Read More »5. 4 basic laws about radiation
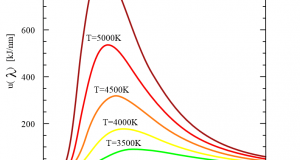
1.Planck Radiation Law Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck, FRS (23 April 1858 – 4 October 1947) Planck’s law describes the electromagnetic radiation emitted by a black body in thermal equilibrium at a definite temperature. The law is named after Max ...
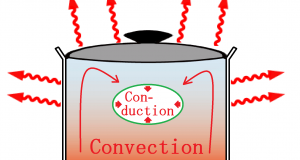
Read More »4. About heating
The thermal energy transfer from higher temperature to lower temperature. Transfer of the thermal energy , there are three principles, Conduction, Convection, and Radiation. In an actual situation, transfer of the thermal energy is performed in the form these three ...
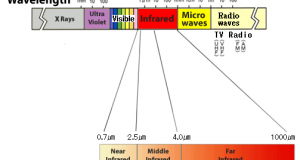
Read More »3. Type of the infrared rays
Infrared Rays are subdivided into several scheme. ISO 20473 specifies the following scheme: Designation Abbreviation Wavelength Near-Infrared NIR 0.78–3 µm Mid-Infrared MIR 3–50 µm Far-Infrared FIR 50–1000 µm The International Commission on Illumination (CIE) recommended the division of infrared radiation into the following ...
Read More »1-9.How to expressions the constant drying period
Constant drying period is the mass of the water which evaporates per unit time and unit surface area. The unit is kg/s㎡. Constant drying rate Jc is expressed by the following equation. kH: Mass transfer coefficient Hw: Saturated absolute humidity ...
Read More »2. About infrared rays
Although it is not visible, because the light with the power which warms a thing existed “outside red”, it was named “infrared rays.” Infrared rays are the same “Electromagnetic waves” as “X-rays”, “Ultraviolet rays”, “Visible light”, “Microwave”, “Radiofrequency wave”, etc. ...
Read More »1. The discovery of the infrared rays
<Science of the Infrared rays -INDEX- > 1. The discovery of the infrared rays 2. About infrared rays 3. Type of the infrared rays 4. About heating 5. 4 basic laws about radiation 6. Absorption rate of infrared rays 7. ...
Read More »1-8.Why is the constant drying period. – Moisture movement in wet material.
Inside moisture material, movement of water (liquid) mainly takes place from the point that moisture content is high to a low point on the surface from an inside in accordance with a slope. There is capillary suction force action, osmotic ...
Read More »1-7.Drying characteristic curve – Relation between a drying rate and moisture content
The drying speed is taken along a vertical axis, average moisture content is taken along a horizontal axis and the above figure is described, it will become a dry characteristic curve. The drying speed is quantity of water evaporating in a ...
Read More »Heat-tech News Letter – Vol. 003
■□■━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━■□■ Heat-tech News Letter – Vol. 003 2014-01-15■━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━■□■ □ INDEX ■1. Guidance of the new product ■2. Guidance of new applications ■3. Support Information ■4. Editor’s note ┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓ ■1. Guidance of the new product┗━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┛ 1-1) [ Heater Controller ] We ...
Read More »1-6.The Local moisture content and the Average moisture content
In general, the moisture content of the material is different in the center and the surface of the material. So, it called the Local moisture content, which is the moisture content of any measurement point. And, it called the Average ...
Read More »1-5.Equilibrium moisture content and Critical moisture content – Influence of temperature and relative humidity
The point which shifts to the Decreasing drying period from the Constant drying period is called the Critical moisture content Wc. The moisture content in which dryness does not advance any more is called the Equilibrium moisture content We. In ...
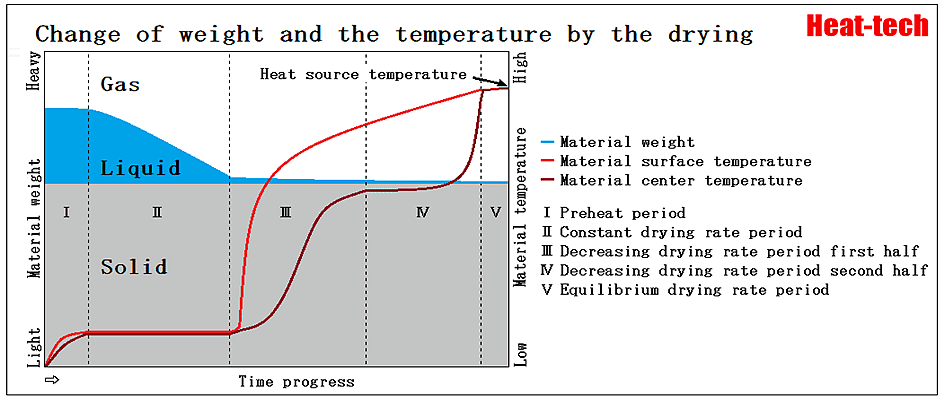
Read More »1-4.Change of weight and the temperature by the drying
As shown in the figure above, wet material is made up the solid , the liquid and the gas as a gap. The weight of material is the sum total of the liquid and the solid. Since the solid weight ...
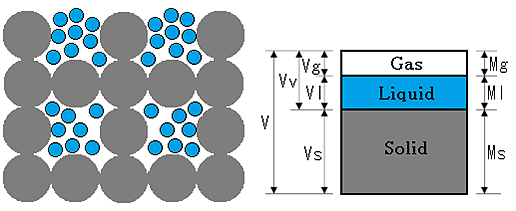
Read More »1-3.How to expressions the moisture in the material
As shown in the figure above, wet material is made up the solid , the liquid and the gas as a gap. Gas Mass : Mg Liquid Mass : Ml Solid Mass : Ms Gas volume : Vg Liquid volume ...
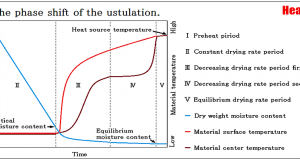
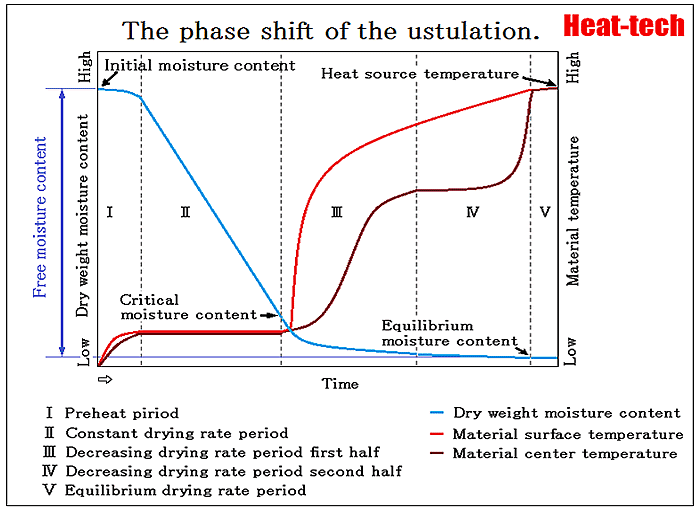
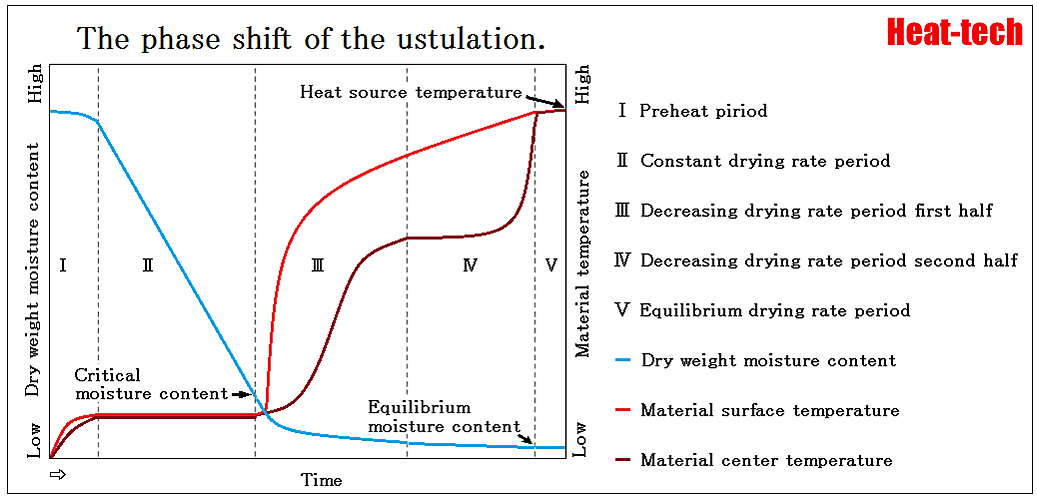
Read More »1-2.The phase shift of the ustulation
Ⅰ.Preheat piriod The material change from initial state to the state that fitted the dry condition. Ⅱ.Constant drying period The surface and the central temperature of materials are kept by the equivalence, and the period which water content decreases linearly ...
Read More »1-1.What is drying
The drying is the process of giving heat and a wind to the moist material containing liquids, a small amount of water and a solvent, evaporating a liquid, removing, and drying a product. As a typical example, in the process ...
Read More »Introduction
More quickly, More uniformly, demanded from the dry process in the manufacture. In order to realize it, it is important to know how heat and a substance will move in the from internal to surface for dryness. In addition, it ...
Read More »The aluminum tube in a glass pipe is heated with a halogen point heater
This video is a heating demonstration of the aluminum tube in a glass pipe is heated with a halogen point heater.
Read More » HEAT-TECH Best Technology Online Shop
HEAT-TECH Best Technology Online Shop