This Video is Demonstration of Heating of 1mm copper plate. Please check the following site for more information.
Read More »Heating of 0.3mm aluminum plate in roll form
This Video is Demonstration of Heating of 0.3mm aluminum plate in roll form. Please check the following site for more information.
Read More »No.23 Cold air temperature drop time
This is a demonstration of measuring and visualizing the temperature drop time of cold air generated by a cold air cooler. Please check the following site for more information.
Read More »No.22 Cold air cooling of a beaker
This video is a demonstration that cools a beaker with a cold air cooler and visualizes the occurrence of frost. Please check the following site for more information.
Read More »Heat-tech News Letter – Vol. 031 2023-01-15
■□■━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━■ □■ Heat-tech News Letter – Vol. 031 2023-01-15 □■ ■━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━■□■ □ INDEX ■1. Guidance of the new product ■2. Guidance of new applications ■3. Movie Library ■4. Editor’s note ┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓ ■1. Guidance of the new product ┗━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┛ 1-1) ...
Read More »No.18 Light source for thin-layer chromatography
[ Problem Point ] A low-cost, easy-to-use analytical method was needed. [ ⇒Kaizen Point ] It was used for pharmaceutical purity tests and follow-up confirmation tests for synthetic experiments. Fluoresces green under UV irradiation at 254 nm For detection by ...
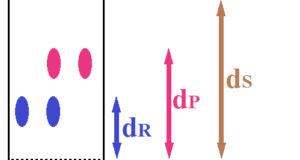
Read More »No.17 Ultraviolet fluorescence method for quantification of uranium ore
[ Problem Point ] A small amount of uranium needed to be quantified. [ ⇒Kaizen Point ] A molten material made by adding a small amount of uranium to sodium fluoride emits a yellow-green fluorescent color when exposed to ultraviolet ...
Read More »No.16 Absorptiometry light source for total protein quantification method
[ Problem Point ] In order to collect samples after measurement, an analytical method that does not use additives was required. [ ⇒Kaizen Point ] Absorbance was measured at a UV wavelength of 280 nm to quantify protein. For a ...
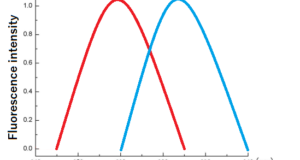
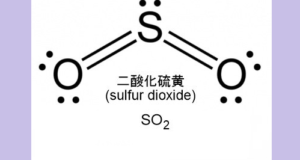
Read More »No.15 Ultraviolet fluorescence method of sulfur dioxide
[ Problem Point ] It was necessary to measure the concentration of sulfur dioxide emitted into the atmosphere. [ ⇒Kaizen Point ] Fluorescence is emitted when the SO2 molecules excited by irradiating the sample with UVC return to the ground ...
Read More »For cold cathode low pressure mercury lamps For Ultraviolet rays point type irradiator UVP-60 Manual power supply controller UVPC-1500V
Color universal design UVPC-1500V series A blue indicator light has been adopted to make it easy for anyone to see. It has a built-in inverter and can light UVP-60 and cold cathode type ultraviolet lamps. Note – Cannot be used ...
Read More »For Ultraviolet rays point type irradiator UVP-30 Manual power supply controller UVPC3.6V
Color universal design UVCP3.6V series A blue indicator light has been adopted to make it easy for anyone to see. A dial is included to allow manual current control of the UVP-30 at 3.6V. Note – Cannot be used for ...
Read More »Ultraviolet point type irradiation device Laboratory-kit LKUVP-60 + UVPC
Focal sizeΦ12 Sterilization UV spot irradiation can be done easily! ◆ Feature ◆ Since it is a kit, user can easily use the UV irradiation device. UV irradiation of 375 nm is possible. UV irradiation of Φ13 can be easily reproduced. The ...
Read More »Ultraviolet point type irradiation device Laboratory-kit LKUVP-30 + UVPC
Focal sizeΦ13 Easily UV point irradiation! ◆ Feature ◆ Since it is a kit, user can easily use the UV irradiation device. UV irradiation of 375 nm is possible. UV irradiation of Φ13 can be easily reproduced. The manual variable power supply ...
Read More »UV Ray line type Irradiator Lab Kit LKUVL-115
Easy UV irradiation! ◆ Features◆ 1). Since it is a kit, user can easily irradiate UV rays. 2). Built-in amplifier makes lighting operation easy. 3). Irradiate 253.7 nm, which has a high sterilization effect, with a large output of 8 ...
Read More »UV point type irradiator UVP-60 series
1.Features of UVP-60 1) UV-C 253.7nm irradiation is possible. 2) UVP-60 is compact and can irradiate a point of φ12 with UV rays. UVP-60 is an ultraviolet point type irradiator that points the light of an ultraviolet lamp with a ...
Read More »Compact UV point type irradiator UVP-30 series
1. Features of UVP-30 1) UVP-30 is compact and can irradiate a point of φ13 with UV rays. UVP-30 is an ultraviolet point type irradiator that points the light of an ultraviolet lamp with a condensing mirror. 2) User can ...
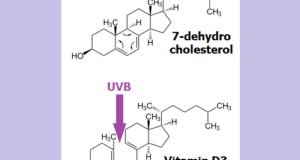
Read More »No.14 Synthesis of vitamin D by UV irradiation
[ Problem Point ] Poor health due to lack of vitamin D. [ ⇒Kaizen Point ] Exposure to ultraviolet rays (UV-B) with a wavelength of around 300 nm for about 10 minutes a day, Vitamin D was synthesized in the ...
Read More »Heating of Φ1mm Titanium Wire
This video is Demonstration of brazing of Aluminum with Halogen Point Heater. Please check the following site for more information.
Read More »Brazing of Stainless Steel Using Halogen Point Heater
This Video is Demonstration of Brazing of Stainless Steel with Halogen Point Heater. Please check the following site for more information.
Read More »Brazing with Halogen Point Heater
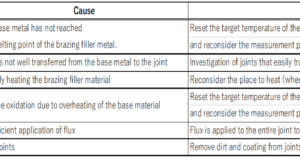
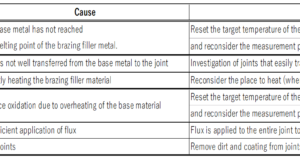
Brazing with Halogen Point Heater As with Air Blow Heater, information on brazing heating with halogen heaters is not very common, so this is an experiment to see to what extent brazing is possible. Overview of Halogen Point Heater Halogen ...
Read More »Brazing with Air Blow Heater
Brazing with Air Blow Heater There are many heating methods for brazing, and representative brazing methods include gas brazing, high-frequency induction brazing, resistance brazing, and arc brazing. Brazing with the Air Blow Heater is not very common, so we experimented ...
Read More »About Brazing
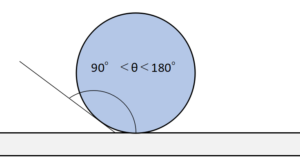
Brazing with Heater About Brazing Brazing with Air Blow Heater Brazing with Halogen Point Heater Brazing with Halogen Line Heater About Brazing Brazing is a welding method like soldering that joins metals together. In brazing, joining is possible without ...
Read More »Brazing of Copper Using Halogen Point Heater
This Video is Demonstration of Brazing of Copper with Halogen Point Heater. Please check the following site for more information.
Read More »Brazing of Aluminum Using Halogen Point Heater
This video is Demonstration of brazing of Aluminum with Halogen Point Heater. Please check the following site for more information.
Read More »Brazing of Aluminum and Copper Using Air Blow Heater
*Check Video is here This video is Demonstration of brazing of Aluminum and Copper with Air Blow Heater. Please check the following site for more information.
Read More » HEAT-TECH Best Technology Online Shop
HEAT-TECH Best Technology Online Shop