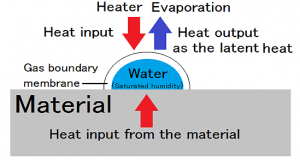
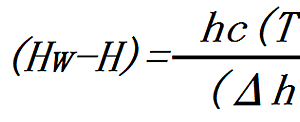Even if it tells “dryness” to a mouthful, there are three kinds of dry work. They are dryness of surface water of adhesion, dryness of the coating film, and internal dryness of material. Since the preceding sections has explained the ...
Read More »No.90 Heat test of bearing
[ Problem Point ] Managing the heat-resistant temperature of grease, it came to carry out a quality assessment and there was nothing. [ ⇒Kaizen Point ] It heated from room temperature to 550℃ with the Air blow heater. The quality ...
Read More »3-6.Importance of dehydration
Energy for evaporating the water 1kg of 20 ℃ is 2454kJ. 1kW/h is 3600kJ so…. 2454kJ is the working time and energy consumption of the same amount running 40 minutes of 1kW motor. Or, the halogen heater 5kw 85% efficiency ...
Read More »3-5.Balance of the process
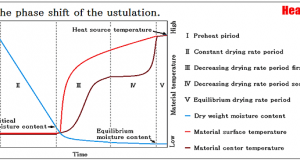
When dry quickly at high speed wet material, deviation of the moisture content and temperature of the material inside will increase. As a result, the critical moisture content is increased, it may cause cracks. When it comes to the state ...
Read More »3-4.Five patterns of the drying curve
As for the Drying characteristic curve of the Decreasing drying rate period, five patterns appear with the characteristic of material. The type of material The composition of material The shape of material The possession state of water A-Type A-type is ...
Read More »3-3.Heat balance equation of the drying
The heat balance is the sum of 4 types heat、which is entering heat, exiting heat, generation of heat, and endothermic. By the law of conservation of energy, the quantity of these (Quantity of heat change of the system) = (Quantity ...
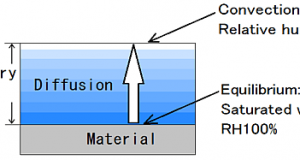
Read More »3-2.Evaporation of water
In order to move water vapor becomes water evaporates, the water vapor pressure difference is required between the air and the convection layer and the surface of the material. Water vapor of the material surface so that the saturated pressure ...
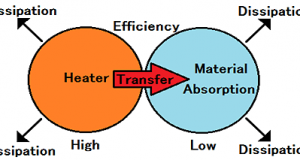
Read More »3-1.Heat transfer and Mass transfer
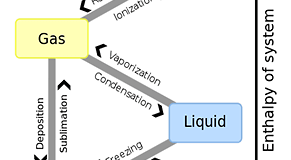
In the classification of thermodynamics, a dry process is a “The open system.” Dryness is “evaporating and separating a liquid from a solid.” Heat and pressure are operated, water is evaporated and it moves. The height of heat is the ...
Read More »2-11.Dew point and Dew point meter
1.Dew point The dew point is the temperature from which condensation begins, when the air containing vapor is cooled. It is also referred to as the dew point temperature. Unit is used to evaluate the K or Kelvin degrees Celsius ...
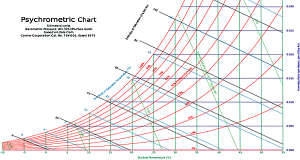
Read More »2-10.The Psychrometric charts
Psychrometric charts A psychrometric chart for sea-level elevation Terminology A psychrometric chart is a graph of the thermodynamic parameters of moist air at a constant pressure, often equated to an elevation relative to sea level. The ASHRAE-style psychrometric chart, shown ...
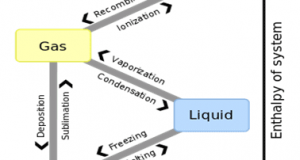
Read More »2-9.Latent heat, Sensible heat, and Evaporation heat ( or Vaporization heat )
The heat which appears in the temperature of a substance and can be observed is sensible heat. The heat unobservable although the state of a substance is changed is latent heat. Sensible heat + Latent heat = Total heat The ...
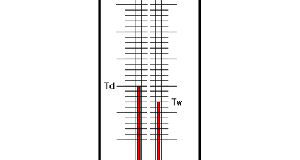
Read More »2-8.The principle of the Psychrometer
If alcoholic disinfection is carried out before injecting, when alcohol evaporates, he will have a cold feeling to because heat is taken. In order for a liquid to turn into gas, energy is required and this energy is called evaporation ...
Read More »2-7.Psychrometer and Hygrometer
2-7-1.Spirits of Dry and Wet Líu Ān (Chinese: 劉安, c.179 – 122 BC) was a Chinese king and advisor to his nephew, Emperor Wu of Han (武帝). The old days of more than 2000 years from now, Concept of humidity ...
Read More »2-6.Relationship of absolute humidity and the relative humidity
We have explained the relative humidity and absolute humidity to 2-5 from 2-1. Let’s check again here. Quantity the water of which exists in the air with absolute humidity Even if it heats air, since the weight of the water ...
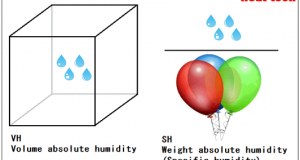
Read More »2-5.Absolute humidity
Absolute humidity Generally, if it is only called “Humidity”, “Relative Humidity =RH” will be pointed out, but it is convenient to use the absolute humidity from which a value does not change in a design or control of a drier ...
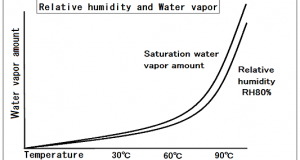
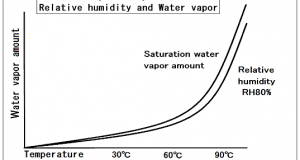
Read More »2-4.Relative humidity RH
Relative humidity RH Relative humidity is the ratio of the partial pressure of water vapor in an air-water mixture to the saturated vapor pressure of water at a prescribed temperature. The relative humidity of air depends on temperature and the ...
Read More »Heating to 1000 ℃ the air by the Air Blow Heater
This video is a demonstration that is heating to 1000 ℃ the air by the Air Blow Heater.
Read More »2-3.Ask for saturation water vapor pressure
The saturation water vapor amount is the representation of g in the mass of water vapor that can be present in the space of 1m3. Absolute humidity volume, saturation water vapor density is also known as, aka. Saturation water vapor ...
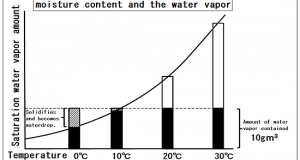
Read More »2-2.There is a limit to the water vapor contained in the air
There is a limit to the amount of water vapor that air can contain. Within the air, water movement may become gas (vapor) from a liquid, that or become liquid from gas (vapor) has been constantly repeated. The temperature that ...
Read More »2-1.What is the humidity?
The Chapter 1 focused on moisture inside material. The Chapter 2 focuses on the moisture emitted in the form of vapor into the air. Definition of the humidity Of humidity, it is a representation of a number the wetness in ...
Read More »1-9.How to expressions the constant drying period
Constant drying period is the mass of the water which evaporates per unit time and unit surface area. The unit is kg/s㎡. Constant drying rate Jc is expressed by the following equation. kH: Mass transfer coefficient Hw: Saturated absolute humidity ...
Read More »1-8.Why is the constant drying period. – Moisture movement in wet material.
Inside moisture material, movement of water (liquid) mainly takes place from the point that moisture content is high to a low point on the surface from an inside in accordance with a slope. There is capillary suction force action, osmotic ...
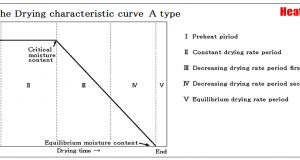
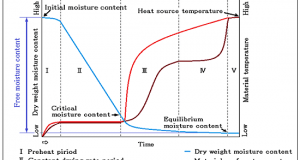
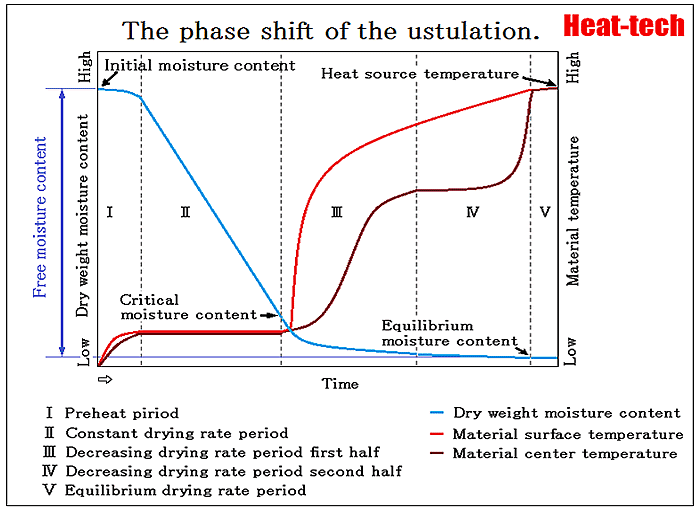
Read More »1-7.Drying characteristic curve – Relation between a drying rate and moisture content
The drying speed is taken along a vertical axis, average moisture content is taken along a horizontal axis and the above figure is described, it will become a dry characteristic curve. The drying speed is quantity of water evaporating in a ...
Read More »1-6.The Local moisture content and the Average moisture content
In general, the moisture content of the material is different in the center and the surface of the material. So, it called the Local moisture content, which is the moisture content of any measurement point. And, it called the Average ...
Read More »1-5.Equilibrium moisture content and Critical moisture content – Influence of temperature and relative humidity
The point which shifts to the Decreasing drying period from the Constant drying period is called the Critical moisture content Wc. The moisture content in which dryness does not advance any more is called the Equilibrium moisture content We. In ...
Read More » HEAT-TECH Best Technology Online Shop
HEAT-TECH Best Technology Online Shop