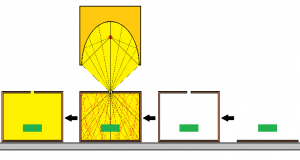
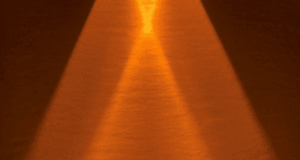
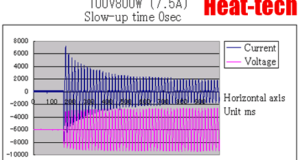
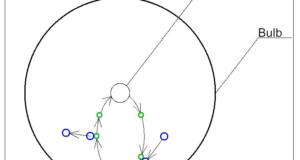
Basic principle Make a small hole in the box and heat it from the outside. Using this heating method, you can also create a high-temperature electric furnace with a simple structure. Assuming that the inner surface of the box has ...
Read More »6-5.High temperature heating method – Dome heating
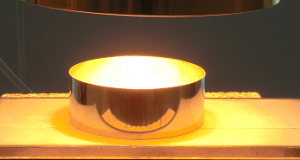
Basic principle A dome cover is used when heating a relatively wide area or heating a plate-like material uniformly. If the dome cover needs to be durable, our condense mirrors can also be used as a dome cover. The light ...
Read More »6-4.High temperature heating method – Frame heating
Basic principle The heating target of frame heating is heated with three elements. 1.Direct heating from heat source 2.Heating by reflected light from the wall 3.Heating by radiant heat on the wall Preventing adverse effects of updraft Open heating also ...
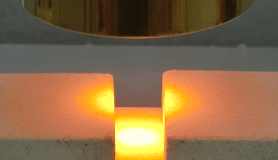
Read More »6-3.High temperature heating method – Groove heating
Basic principle This figure shows the case where the object to be heated is small and equal to or smaller than the condensing diameter (width) of the halogen heater. Make a groove in a simple way and place the object ...
Read More »6-2.How to heat the object to a higher temperature and uniformity?
1. Reduce the distance The closer the distance from the heater to the object to be heated, the higher the temperature it can be heated to. Even in condensed heating, the shorter the condensed distance, the higher the temperature can ...
Read More »6-1.About the high-temperature heating method
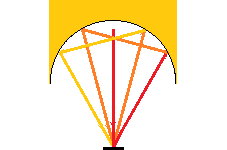
Overview of the high-temperature heating method Concentrating heating using a halogen lamp uses a condensing mirror to concentrate light energy on the object to be heated to a high temperature. Of the light incident on the object to be heated, ...
Read More »4-6.About the seal of halogen lamps
Like incandescent lamps, halogen lamps need to have a sealed structure that prevents the enclosed gas from leaking to the outside. Also, in halogen lamps, the temperature of the valve must be 250 degrees or higher as a condition for ...
Read More »4-5.Quartz glass bulb for halogen lamps
About quartz glass bulbs Due to the halogen cycle, halogen lamp bulbs must be heat-resistant glass with a temperature of 250℃ or higher when lit. In addition, the inert gas and halogen gas in the bulb are sealed at a ...
Read More »4-4.Heat treatment of tungsten
About heat treatment of tungsten Tungsten has a melting point of 3422 ℃, which is the highest melting point of metals. From a machining perspective, the ductile-brittle transition temperature is high and low temperature brittleness is seen at room temperature. ...
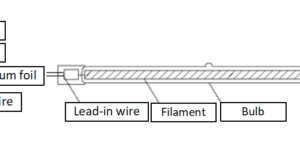
Read More »4-3.About filament coil
Tungsten, which has the highest melting point of metals, is used as the filament. In order to suppress heat loss due to the halogen gas to be enclosed, a filament that has been improved from a straight line and made ...
Read More »4-2.Types and mechanisms of halogen lamp gas
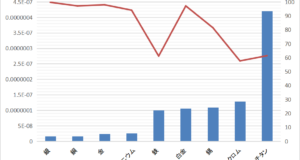
Halogen lamp gas type Halogen lamps are incandescent lamps that contain an inert gas and a small amount of halogen gas inside the lamp. Inert gas Inactive gas includes helium (He 4.00g/mol), neon (Ne 20.18g/mol), (nitrogen (N2 28.02 / mol)), ...
Read More »5-4.Proper use of near-infrared heating and far-infrared heating
A halogen heater is used for radiant heating of near infrared rays. Of the electromagnetic waves radiated from a heating element at about 3000℃, the maximum wavelength is about 1μm in the near infrared region. A convex parabola is drawn ...
Read More »5-3.About the Wavelength of Heat Radiation
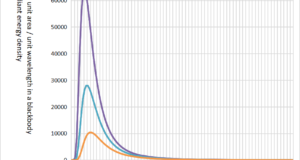
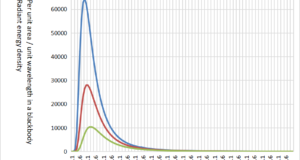
An object with an absolute temperature of 0K (Kelvin) or higher radiates a wavelength corresponding to the temperature of the object as an electromagnetic wave. The object that received this electromagnetic wave has received heat. This transfer of heat is ...
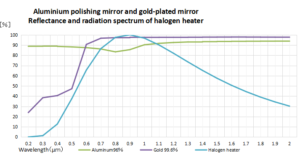
Read More »5-2.About the Type of Reflection
There are two main types of reflection. Regular reflection Regular reflection refers to reflection that holds the “law of reflection” in which the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection of light incident from a light source are equal. ...
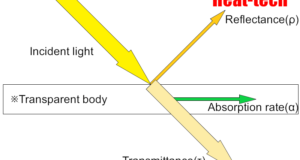
Read More »5-1.Light Reflectance,Transmittance, Absorption Rate = Emissivity
Every substance is made up of very small particles. The molecules that make up that substance have different molecular motions depending on the temperature. A molecule is made up of several atoms linked by chemical bonds, and any bond. Each ...
Read More »4-1.Development History Up to Halogen Lamps
Development of carbon filament Halogen lamps evolved from incandescent light bulbs. Carbon fiber was used for the filament of the early heat-generating light bulbs. Metal filaments such as osmium and tantalum were being developed, but they did not reach the ...
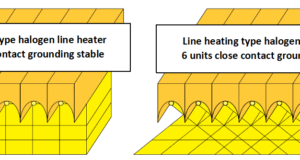
Read More »3-8.Wide Range of Plane Heating with Line Heating Type Halogen Line Heater
By arranging multiple line heating types and lengthten the focal length from the rated distance, the condensing width can extend and a wide range of heating can be performed. (Out focus) Of course, even with the plane heating type, a ...
Read More »3-7.Halogen Line Heater Lifespan
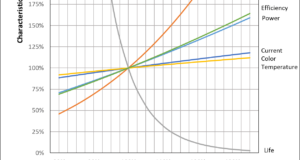
The lifespan of a halogen lamp depends on the voltage used. The rated voltage is defined as 100%, and if the voltage is lowered by 10%, the lifespan is extended by about 3 times, and if the voltage is increased ...
Read More »3-6.Halogen Line Heater cooling
Continuous use of halogen line heaters always requires cooling. This is because the heat resistance temperature of the lamp seal is 300°C. Avoid using it at the heat-resistant temperature limit, and be sure to cool it down. If user heat ...
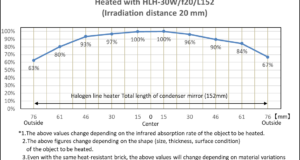
Read More »3-5.Temperature Distribution of Halogen Line Heater
3-4.Focal length and focal width of Halogen Line Heater
Relationship with the light collecting diameter of the Halogen Line Heater First of all, we will define the words. “Focus width” is the narrowest width of condensing distance. And focus width is rated width. “Focal length” is the condensation distance ...
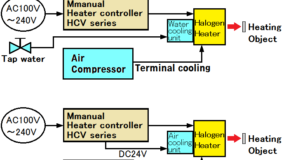
Read More »3-3.How to use Halogen Line Heater
[Manual setting with cooling unit installed] [Automatic setting with cooling unit installed]
Read More »3-2.Basic structure of Halogen Line Heater
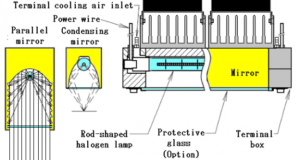
[Basic structure of Halogen Line Heater] Halogen Line Heater consists of cooling unit, lamp unit, Condensing mirror unit, terminal box, and protective glass. Most of the composition covers an elongated lamp and is occupied by a condensing mirror. Quartz glass ...
Read More »3-1.Overview of Halogen Line Heaters
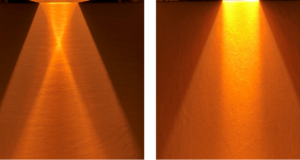
Halogen Line Heater (Line Condensing Type) Halogen Line Heater (Plane Condensing Type) Halogen Line Heaters convert the electricity of rod-shaped halogen lamps into light, A heater that uses a condensing mirror to concentrate the light in a line or plane ...
Read More »2-7.Halogen Point Heater Lamp lifespan
The lifespan of a halogen lamp depends on the voltage used. The rated voltage is defined as 100%, and if the voltage is lowered by 10%, the lifespan is extended by about 3 times, and if the voltage is increased ...
Read More » HEAT-TECH Best Technology Online Shop
HEAT-TECH Best Technology Online Shop